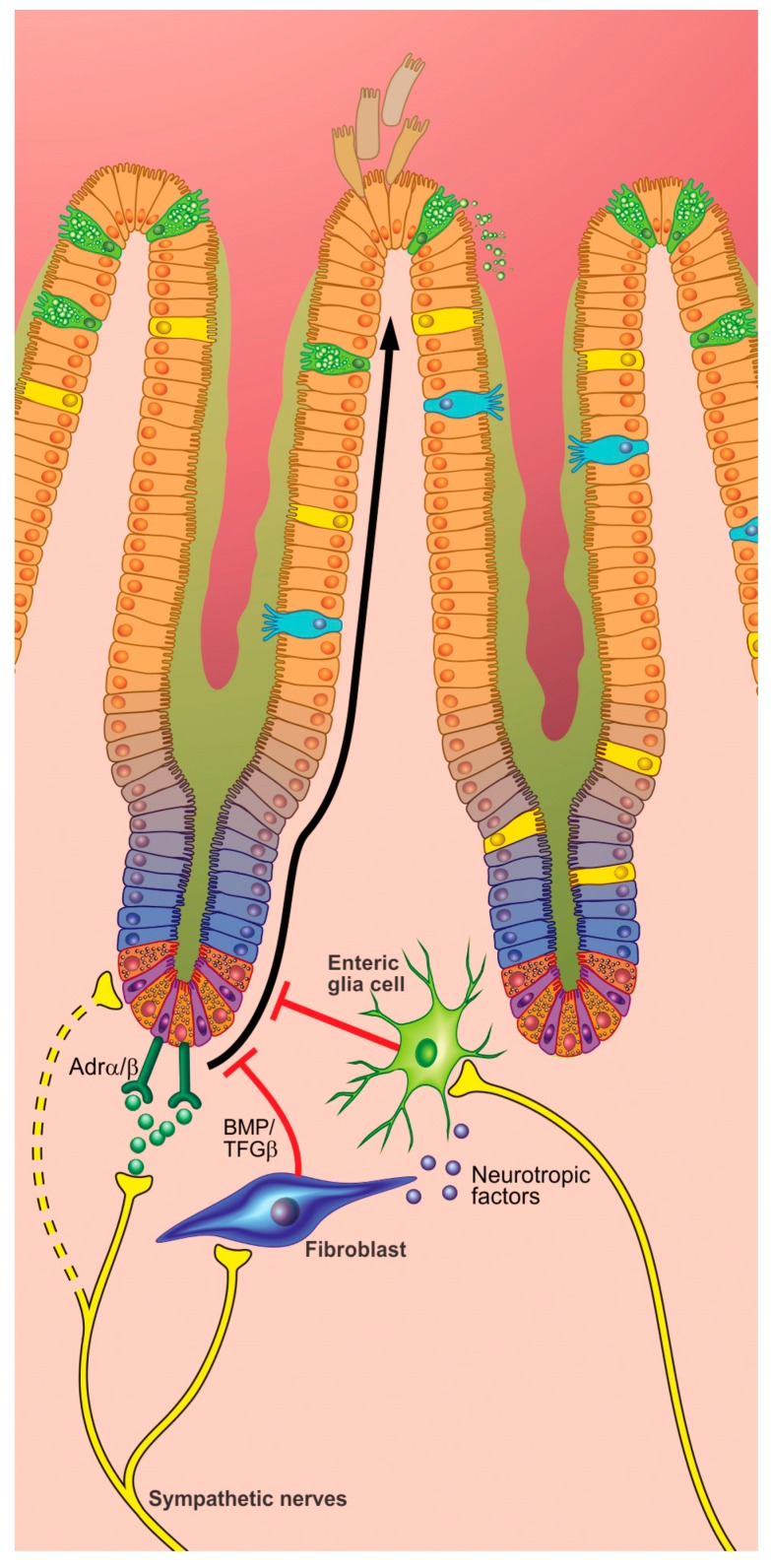
Figure 4.
Proposed model of innervation of the intestinal crypt. Sympathetic nerves affect the proliferation in the crypt in multiple ways. Sympathetic neural activity inhibits proliferation through fibroblasts (that produce bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and transforming growth factor (TGF-β)) and enteric glia cells that express adrenergic receptors. Enteric glia cells also produce neurotrophic factors that are critical in the growth, survival, and differentiation of nerves. In addition, adrenergic receptors are present on cells within the crypt, suggesting that sympathetic neural activity affects the proliferative processes directly.