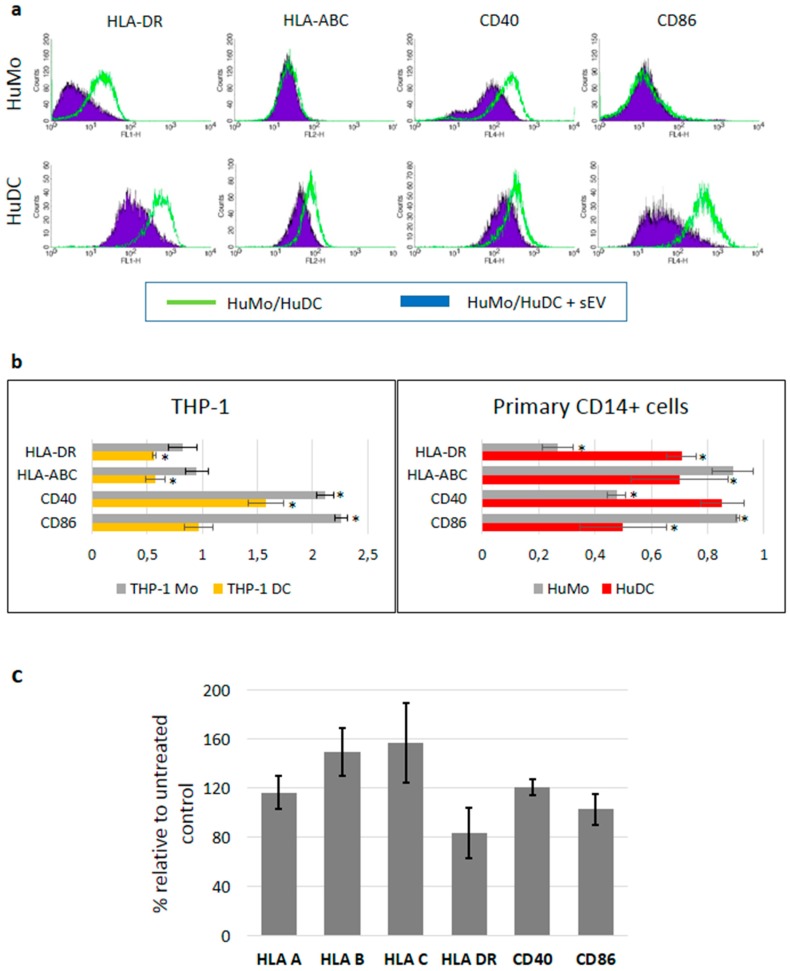
Figure 3.
Melanoma cell-derived sEVs modulate the immune receptor expression on APCs. (a) Upper panel: The cell surface expression of MHC class I, II, CD40, and CD86 of CD14+ primary human monocytes (HuMo) was measured by flow cytometry (green lines). Overlaid are the histograms after exposure to A375 melanoma-derived sEVs for 48 hours (filled violet peaks; representative of n = 6). Lower panel: HuMo were differentiated into DCs (HuDC) and exposed to sEVs for 48 hours and the cell surface expression was analyzed by flow cytometry, as above (representative of n = 3). (b) The mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) of the surface expression of MHC class I, II, CD40, and CD86 after exposure to melanoma-derived sEVs was related to the MFI of unexposed cells. Both monocytes and DCs derived from either the THP-1 cell line (left diagram) or primary human CD14+ cells (right diagram) were used in the experiments. At least three independent experiments were conducted for each cell type and significant differences were marked by asterisks (Student’s t-test). (c) The mRNA expression levels in DC cells derived from the peripheral blood of healthy donors treated with A375-derived sEVs relative to untreated control cells. Mean values and standard deviations are shown from three independent experiments. The differences between samples after sEV exposure and untreated controls did not reach statistical significance (Student’s t-test).