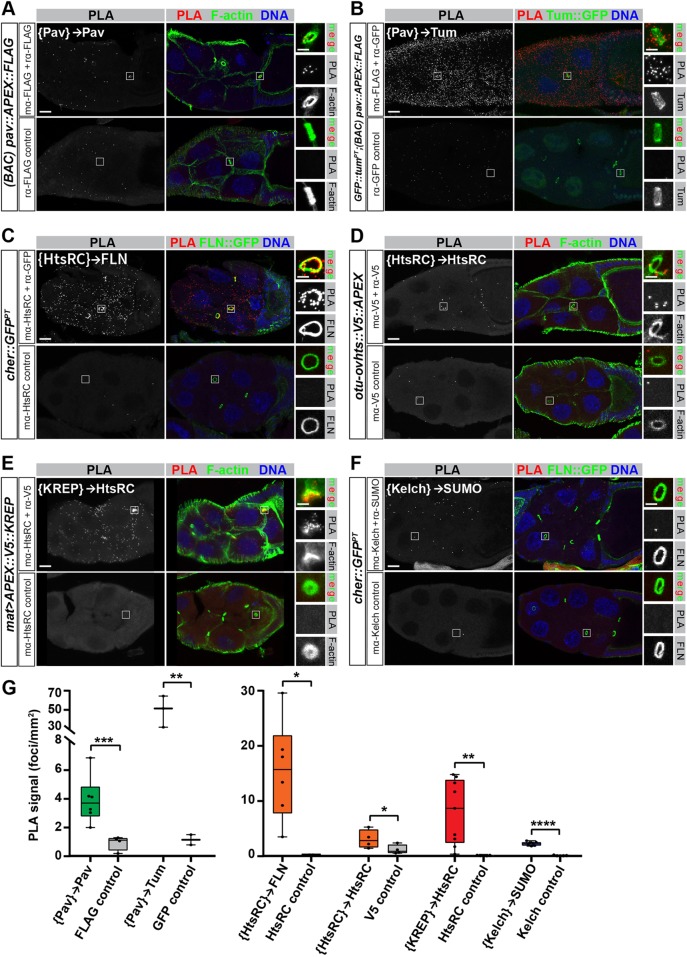
Fig. 6.
In situ proximity ligation assay confirms close-proximity interactions between RC-APEX bait proteins and respective prey. (A-F) Proximity ligation assays were performed on cryosectioned ovary tissues of the indicated genotypes to test for close-proximity interactions between different protein pairs, listed in white text in the top left of each panel (with brackets around the RC-APEX bait protein and an arrow pointing to the prey protein). A positive PPI was indicated by the presence of PLA signal (left panels), which was visualized by fluorescent probes that bind to the PLA DNA product. Antibodies used for each reaction are indicated on the left, and the bottom panels served as negative controls because one antibody was omitted. Boxed insets contain RCs showing F-actin, GFP::Tum, or Filamin::GFP (FLN::GFP) patterns, as indicated in the panel labels. The protein pairs tested exhibited a distinct RC signal, with the exception of the {Kelch}→SUMO (F) interaction, which was mostly dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. (G) Positive PLA foci in each egg chamber imaged were counted in FIJI using thresholding and particle analysis, and graphed as a function of egg chamber unit area. Student's t-test was used to compare the number of PLA foci per unit area in experimental samples versus controls. *P≤0.1; **P≤0.05; ***P≤0.001; ****P≤0.0001. Scale bars: 20 μm (main panel) and 5 μm (insets).