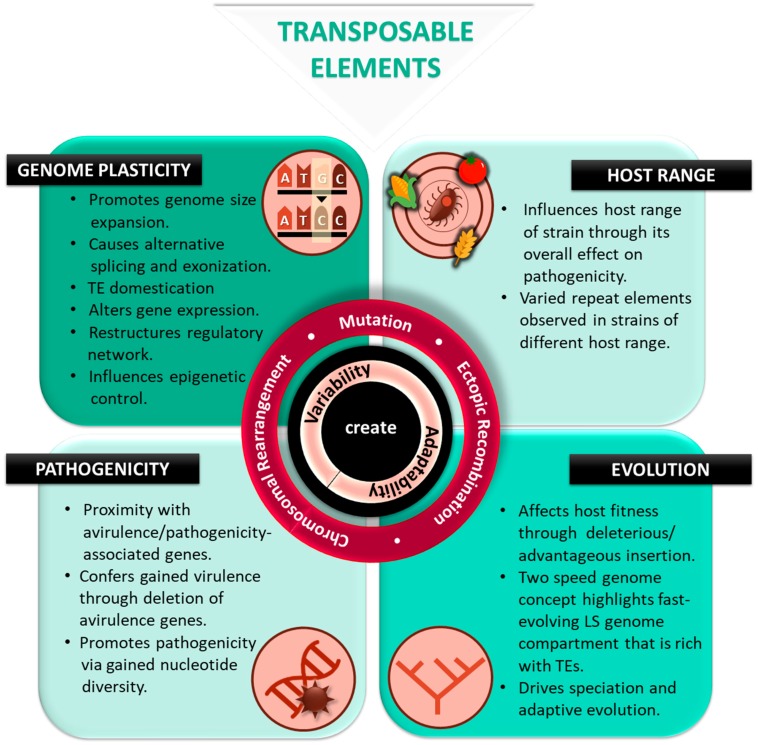
Figure 2.
The role of transposable elements in affecting genome plasticity, influencing host range and pathogenicity, and shaping evolution of phytopathogens. Transposable elements generate genetic variability that can contribute to host adaptation to its surroundings. The mechanisms involved include TE-mediated mutation, ectopic recombination and chromosomal rearrangement. Collectively, TEs can influence agriculturally relevant traits exemplified by observations made in rice pathogens and other fungal phytopathogens. (Source: Credit Ilakiya Kumar).