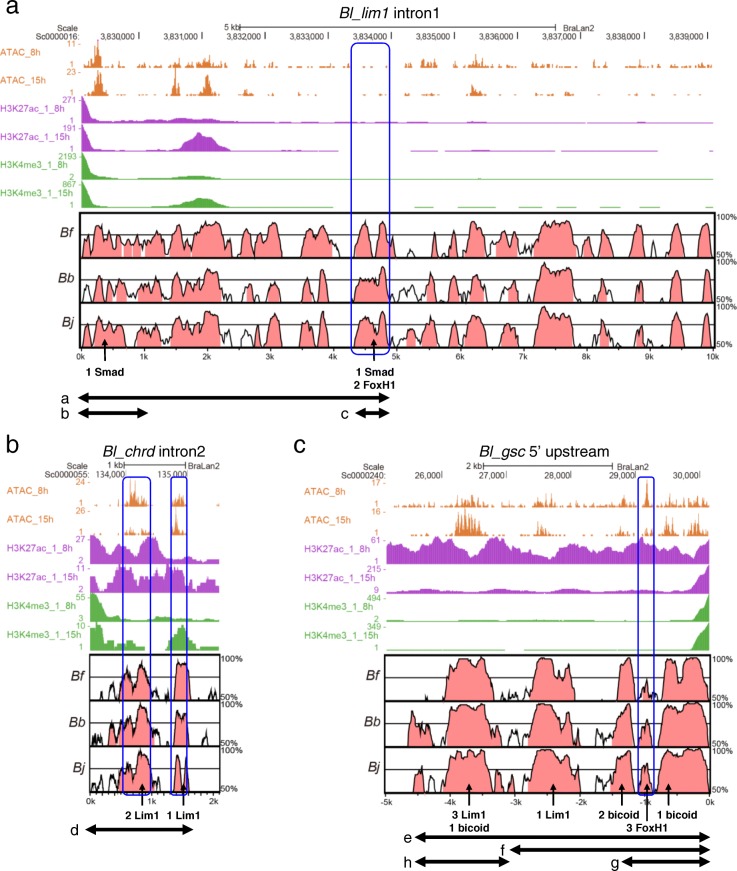
Fig. 3.
Epigenetic data from B.lanceolatum embryos and sequence comparisons between B.lanceolatum, B. floridae, B. belcheri, and B. japonicum. a ATAC-seq, H3K27ac ChIP-seq, and H3K4me3 ChIP-seq data from early gastrula (8 hpf) and early neurula (15hpf) in Bl_lim1 intron 1 are represented with Vista plot of Bl_lim1 intron 1 vs Bf_lim1 intron 1, Bb_lim1 intron1 and Bj_lim1 intron 1. Regions with 50–100% identity were shown and conserved non-coding sequences (CNSs) were colored in red. The number of Smad motifs and FoxH1 motifs in CNSs is shown as indicated by arrows. b Epigenetic data in Bl_chrd intron 2 are represented with Vista plot of Bl_chrd intron 2 vs Bf_chrd intron 2 Bb_chrd intron 2 and Bj_chrd intron 2. The number of Lim1 sites in CNSs is indicated by arrows. c Epigenetic data in Bl_chrd intron 2 are represented with Vista plot of the − 5 kb region of Bl_gsc vs those of Bf_gsc, Bb_gsc and Bj_gsc. The number of Lim1, bicoid, and FoxH1 sites in CNSs is shown as indicated by arrows. a–h, Regions used for reporter assays. Blue boxes indicate putative CRMs analyzed in reporter assays (Figs. 4 and 5). Additional file 1: Figure S1 shows sequence alignment of them (see Additional file 1)