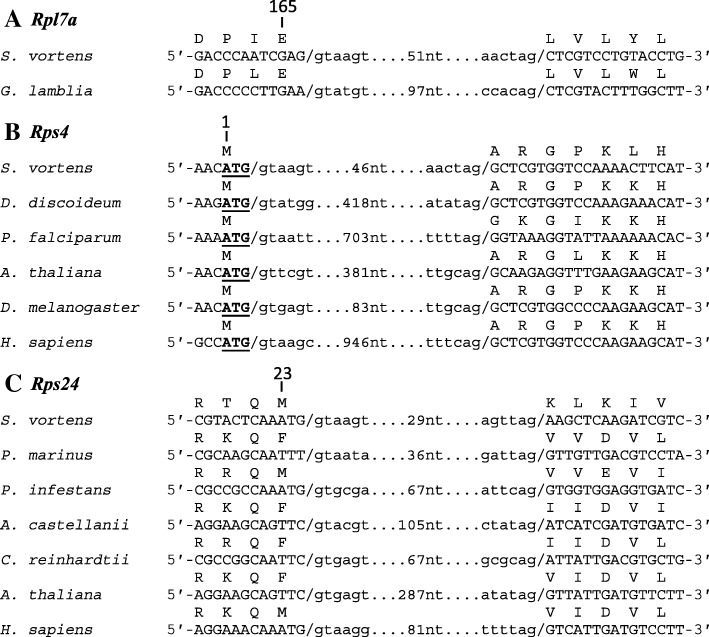
Fig. 5.
Conservation of Rpl7a, Rps4 and Rps24 intron insertion sites. Gene sequences from representative eukaryotes containing Rpl7a (a), Rps4 (b) and Rps24 (c) spliceosomal introns are aligned with slashes (/) representing intron-exon boundaries; intronic sequences in lower case and exonic sequences in uppercase. The number of nucleotides between splice site sequences is indicated. Translated amino acid sequences are shown above the first nucleotide of each codon and the start ‘ATG’ codons for the Rps4 coding sequences are underlined. Amino acid positions for each protein are indicated based on the H. sapiens orthologs. NCBI accession numbers for (a) Rpl7a - S. vortens [NCBI Trace Archive:ti|2,141,515,448], G. lamblia [GenBank:NW_002477099], b Rps4 - S. vortens [ti|2,141,550,682], D. discoideum [NC_007088], P. falciparum [NC_004315], A. thaliana [NC_003071], D. melanogaster [NT_037436] and H. sapiens [NC_000023] and (c) Rps24 – S. vortens [ti|2,141,541,737], P. marinus [NW_003201404], P. infestans [NW_003303749], A. castellanii [NW_004457654], C. reinhardtii [NW_001843791], A. thaliana [NC_003074] and H. sapiens [NC_000010]