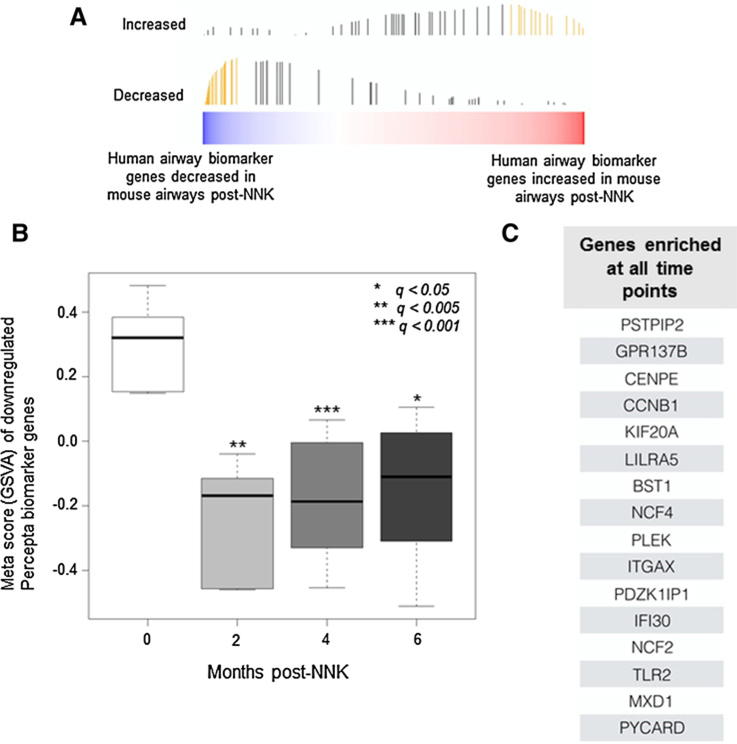
Figure 4.
Human to mouse cross-species analysis of a human bronchial genomic classifier for lung cancer detection. A, A recently reported human bronchial 232-gene classifier (9) was analyzed by GSVA (see Supplementary Methods) in the identified mouse airway profiles that were found to be modulated in vivo following NNK exposure (bar heights correspond to running enrichment score calculated in GSVA and yellow bars correspond to the leading edge subset). B, Meta scores were plotted based on GSVA of a 56-gene leading edge set from the Percepta classifier that is downregulated in airways of human smokers with lung cancer relative to cancer-free smokers and concordantly decreased in the temporal mouse airway brushings. Meta scores were derived and plotted for conserved markers, which were concordantly downregulated at 2, 4, or 6 months after NNK treatment. Statistically significant differences among the different time points were based on a q-value cutoff (*, < 0.05; **, < 0.005; ***, < 0.001). C, GSEA (see Materials and Methods) of the 232-gene human classifier was performed to identify, from the human biomarker, a gene set that was concordantly enriched in the mouse airway samples across all time points.