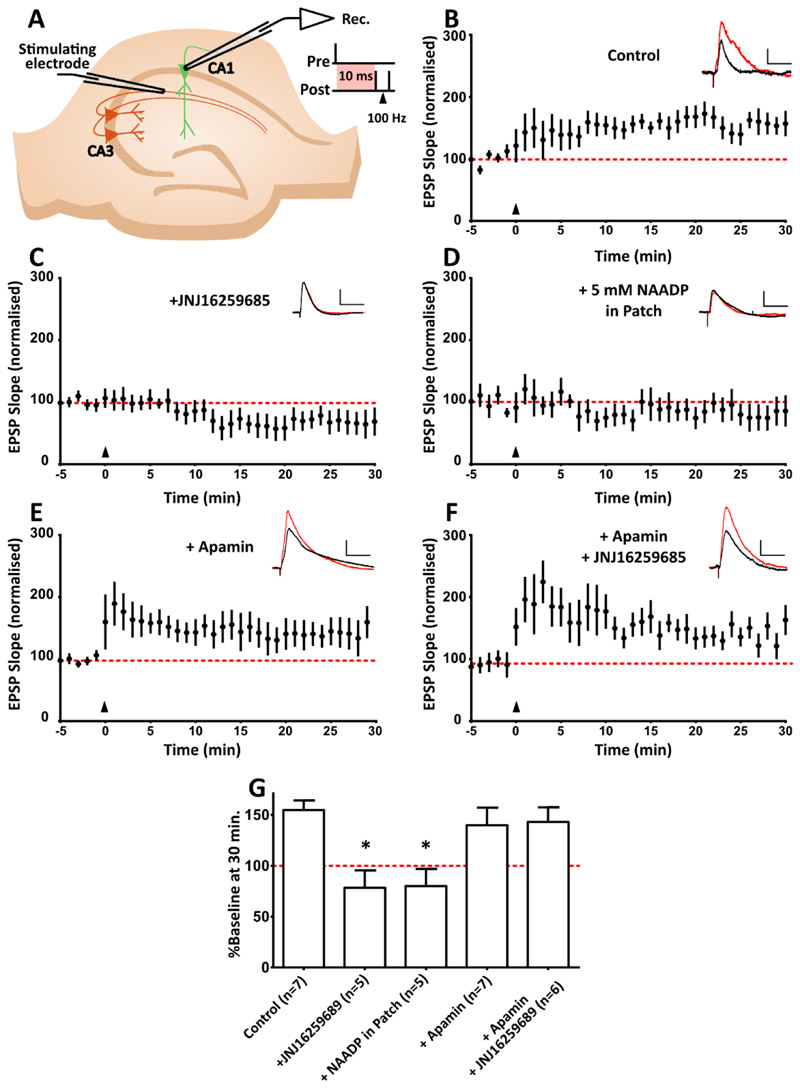
Figure 6. In CA1 pyramidal neurons, mGluR1-dependent synaptic plasticity requires inhibition of SK channels via NAADP signalling.
(A) A causal spike-timing-dependent plasticity protocol was used to induce mGluR1-dependent LTP, in which one causal presynaptic stimulation is paired with two backpropagating action potentials (100 Hz), at a 10 ms interval. The induction protocol is delivered where t = 0, indicated by the black triangles. Example EPSP traces before (black) and after (red) STDP induction are shown at the top right of each graph. Scale bar, 5 mV x 50 ms. This STDP protocol produces LTP lasting at least 30 min (n=7 cells). (B) LTP in the STDP protocol described in (A) with mGluR1-specific antagonism with JNJ16259685 (300 nM; n=5 cells). (C) LTP as described in (A) upon prevention of NAADP/acidic store Ca2+ signalling with a desensitizing concentration of NAADP (5 mM; n=5 cells). (D) Magnitude of LTP upon induction of STDP in the presence of SK channel antagonist apamin (200 nM; n=7 cells). (E) LTP as described in (A) in the presence of apamin and JNJ16259685 (300 nM; n=6 cells). (F) Mean change in synaptic strength at 25-30 min, expressed as a % of the baseline. Data are means ± SEM, n = single cell. * P < 0.05 by Kruskal-Wallis and post hoc Dunn’s tests.