Figure 2. Pathways commonly associated with survival of LSCs from AML, CML, and MDS patients.
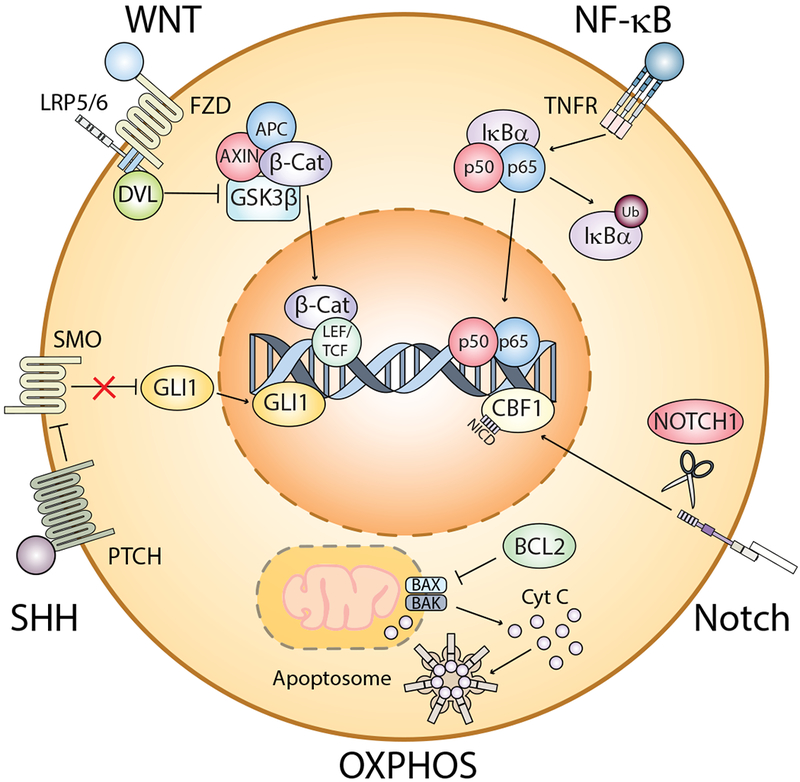
The illustration summarizes some of the major pathways commonly activated in LSCs, including WNT/β-catenin, NF-κB, Sonic hedgehog (SHH), Notch, and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), which is facilitated by upregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein, BCL-2. All of these pathways can be activated through various mechanisms. To date, the leading commonality among stem cells from each disease is a reliance on OXPHOS. AML, acute myeloid leukaemia; APC, adenomatous polyposis; β-Cat, beta-catenin; BAK, BCL2 homologous antagonist killer; BAX, BCL2-associated X protein; BCL2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CBF1, core binding factor 1;CML, chronic myeloid leukaemia; Cyt C, cytochrome c; DVL, dishevelled; FZD, frizzled; GLI1, glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1; GSK3β, Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta; IκBα, nuclear factor-kappa B inhibitor alpha; LEF, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; LRP5/6, low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; LSC, leukaemic stem cell;MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; SMO, smoothened; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NICD, notch intracellular domain, OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PTCH, patched; SHH, sonic hedgehog; STCF, T-cell factor; TNFR, tumour necrosis factor receptor; Ub, ubiquitin.
