Figure 3. Energy dependencies and cell surface molecules being targeted in active clinical trials or in preclinical studies.
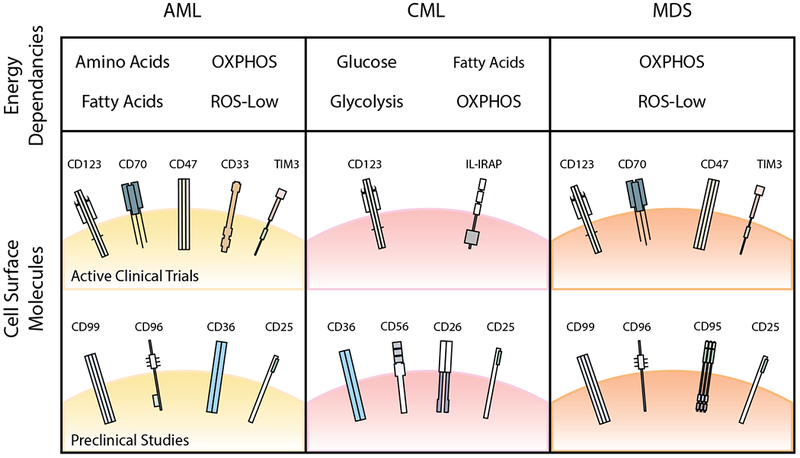
Identifying pathways that are commonly targetable in AML, CML, and MDS will allow for greater clinical utility in the treatment of myeloid malignancies. Here, we summarize some of the energy dependencies and cell surface molecules that are currently being targeted in clinical trials or have been identified to be upregulated in AML, CML, or MDS in preclinical studies. Some of these targets are common across the three disease entities, including oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and CD123. Commonalities between AML and CML LSCs include fatty acid metabolism and CD36, whereas commonalities between AML and MDS LSCs include CD47, TIM3, CD25, and CD99. AML, acute myeloid leukaemia; CML, chronic myeloid leukaemia; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
