Figure 1. Hsd17b4 interacts and colocalizes with ceramide.
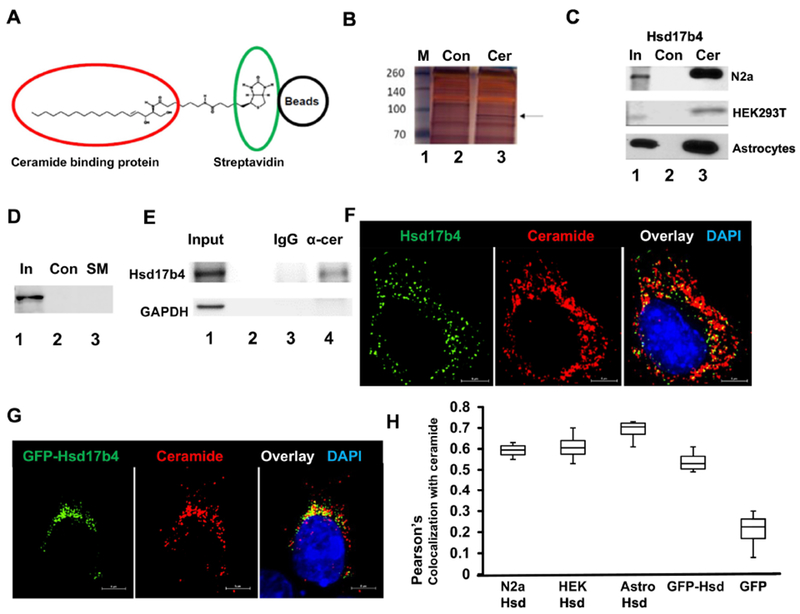
A. Principle of isolating ceramide binding proteins (red circle) by affinity chromatography using biotinylated ceramide immobilized on streptavidin (green circle) agarose beads (black circle). B. Protein interacting with ceramide was isolated using ceramide beads as shown in A. Protein was then separated by SDS-PAGE and silver-stained (Lane 3). Arrow indicates protein excised from the gel and further analyzed by mass spectrometry. Lane 2 shows control sample obtained with biotin-bound control beads. Lane 1, marker. C. Protein isolated from N2a cells, astrocytes, and HEK293T cells as in B, followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using antibody against Hsd17b4 (Lane 3). Lane 2 shows controls prepared as in A. Lane 1 shows input for control and ceramide beads. D. Affinity chromatography of protein from HEK293T cells using biotinylated sphingomyelin immobilized on streptavidin agarose beads. E. Coimmunoprecipitation of Hsd17b4 with α-ceramide IgG used to pull down ceramide-containing vesicles from HEK193T cells. Lane 1, input; lane 2, empty; lane 3, output control rabbit IgG; lane 4, output α-ceramide IgG. Immunoblot for GAPDH was used as negative control. F. Immunocytochemistry using N2a cells and antibodies against Hsd17b4 (green) and ceramide (red). G. HEK293T cells ectopically expressing EGFP-Hsd17b4 (green) were subjected to immunocytochemistry using antibody against ceramide. H. Colocalization analysis using Nikon NIS Elements program (Pearson’s coefficient) on immunocytochemistry for Hsd17b4 (or ectopically expressed EGFP-Hsd17b4) and ceramide in cell types as indicated in image legend. N=4. P<0.01
