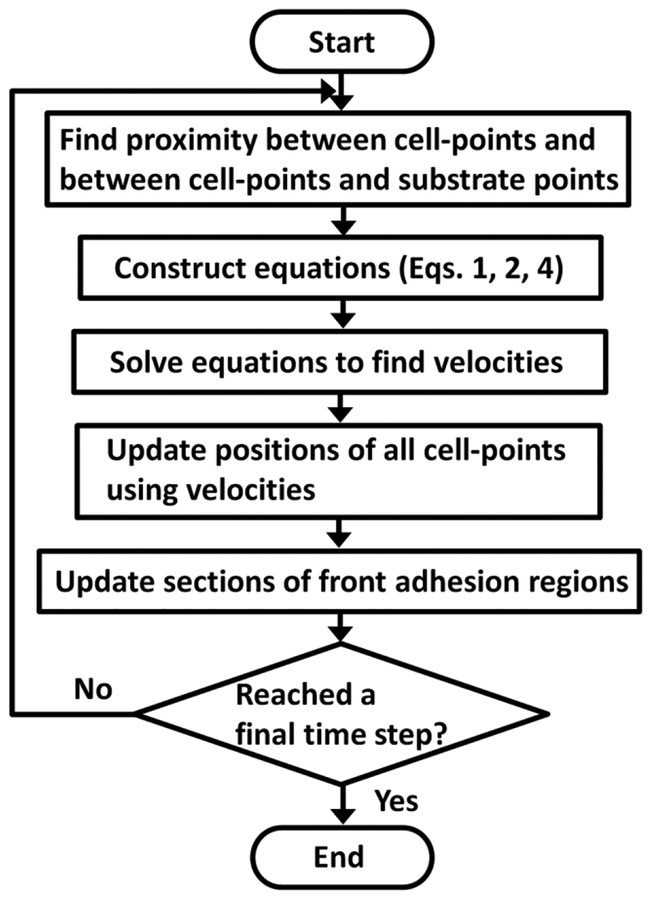
Fig. 2.
Overall flow of computations. Neighboring pairs of cells are identified, and substrate points are assigned to active adhesion regions of cell-points. Based on the identified proximity, the matrix equation is constructed using Eqs. 1, 2, and 4. Then, the matrix equation is solved to find velocities of all cell-points. Positions of all cell-points are updated using the velocities for a next time step. Finally, the activation and deactivation of sections of the front adhesion regions are considered. These steps are repeated until a final time step