Figure 2.
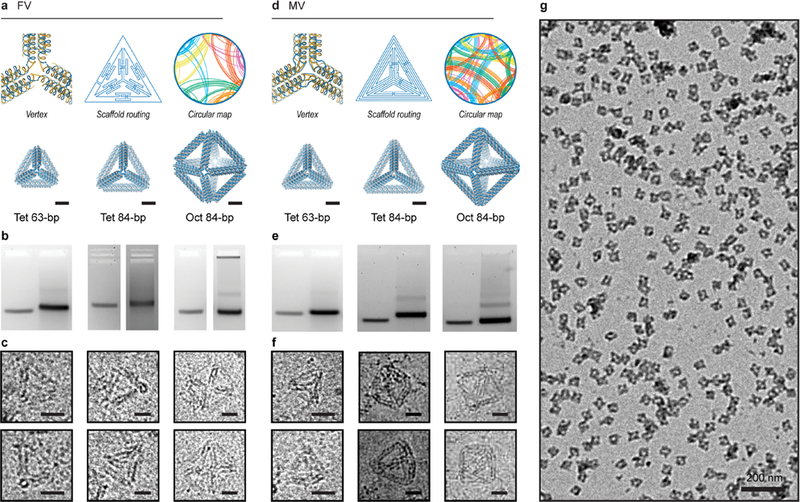
Validation of 6HB DNA-NP origami objects synthesized using TALOS sequence designs. (a–c) In the FV case, the routed structure is generated such that each wireframe edge is connected covalently to its neighboring edges by one scaffold and staple crossing. A circular map is rendered, in which the outer circle representing the scaffold has points assigned in the center of each double-stranded DNA domain with staple connections between regions rendered as lines traversing the circle (see also Figures S14–S18). Characterization of folding for FV tetrahedra of 63-bp and 84-bp edge lengths and an FV octahedron of 84-bp edge length with agarose gel mobility shift assays ((b); uncropped gel images in Figure S48) and cryo-EM (c). (d–f) In the MV case, the routed structure is generated such that each wireframe edge is connected covalently to its neighboring edges by three scaffold and staple crossings. Characterization of folding for MV tetrahedra of 63- and 84-bp edge lengths and an MV octahedron of 84-bp edge length with agarose gel mobility shift assays ((e); uncropped gel images in Figure S48) and cryo-EM (f). (g) Wide-field TEM micrograph shows monodisperse MV octahedra of 84-bp edge length (see also Figures S51–S64). Scale bars are 5 nm in atomic models and 20 nm in cryo-EM and 200 nm in the wide-field TEM.
