Figure 1: EEG samples in hyperkinetic movements.
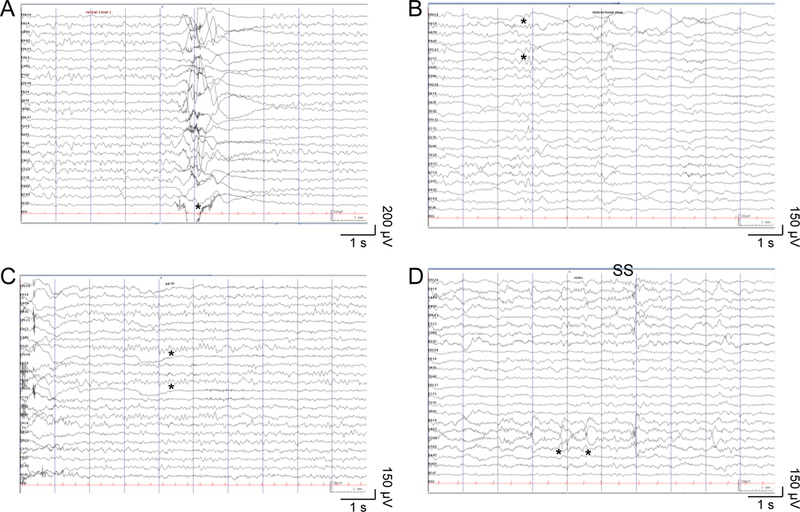
(A) Paroxysmal hyperkinetic movement (*) with no ictal epileptiform electrographic correlate. (B) Occasional poorly-formed bilateral frontal sharp waves (*) in non-REM sleep. (C) Normal 9 Hz alpha posterior dominant rhythm (*) during relaxed wakefulness with eyes closed. (D) Normal symmetric and synchronous sleep spindles (SS) and vertex waves (*) in non-REM sleep. Ceegraph EEG: anterior-posterior bipolar montage, sensitivity 15 μV/mm, time scale 30 mm/s, LFF 0.05 Hz, HFF 70 Hz.
