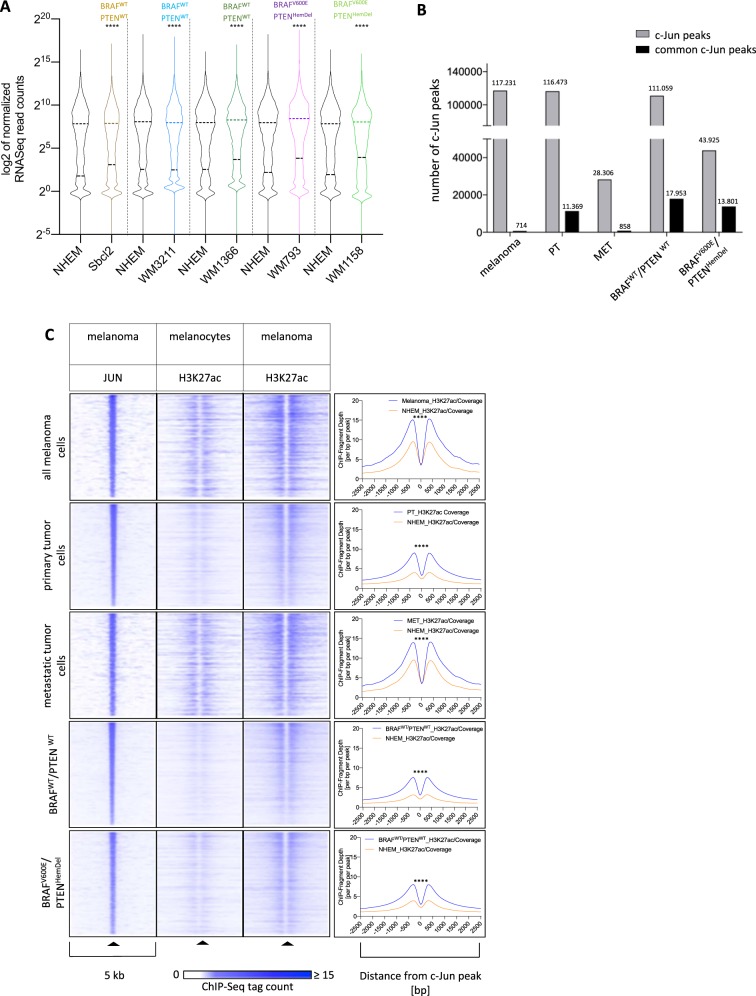
Fig. 2. C-Jun significantly influences gene expression alteration in malignant melanoma.
a All sequenced melanoma cell lines show significant differences in gene expression due to the regulatory activity of c-Jun compared to NHEMs. Violin blots display the interquartile ranges (25–75%) with an intersection as the median; Significantly different distributions in pairwise comparisons are indicated (****P < 0.0001, Wilcoxon test, two-sided). b Clustering of c-Jun peak sets by PTEN expression status revealed a correlation between c-Jun activity and PTEN expression. c Heat maps and histograms of ChIP-Seq tag counts of the histone acetylation status (H3K27ac) in a 5-kb wide range around c-Jun peaks. Regions centered on c-Jun-bound regions were clustered according to their H3K27ac ChIP-Seq profiles in melanoma and NHEMs, illustrating a high acetylation rate around the genomic c-Jun peaks in melanoma and a low rate in NHEMs (****P < 0.0001, Wilcoxon test, paired, two-sided)