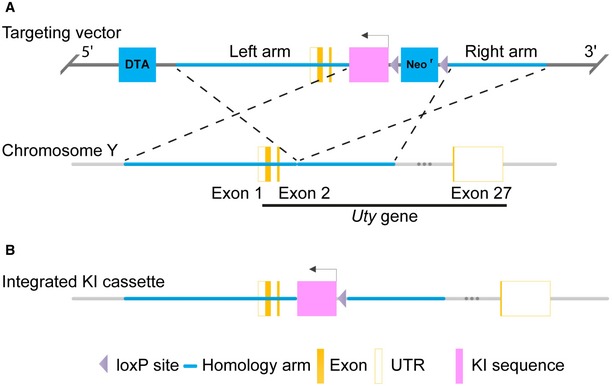
Mouse genomic fragments containing homology arms to the
Uty gene located on mouse chromosome Y were amplified from a BAC clone and sequentially assembled into a targeting vector along with negative and positive selection markers (DTA and Neo, respectively). There are only few mice reported with a transgene on the Y chromosome, one of which is on the
Uty gene
28, and thus, we chose to target the KI cassette into this gene. The KI cassette, encoding the gRNAs targeting genes
Atp5b,
Cdc20, and
Casp8, each expressed from a U6 promoter, was inserted into the targeting vector, which was designed to integrate in reverse orientation of the 2
nd exon of the
Uty gene.