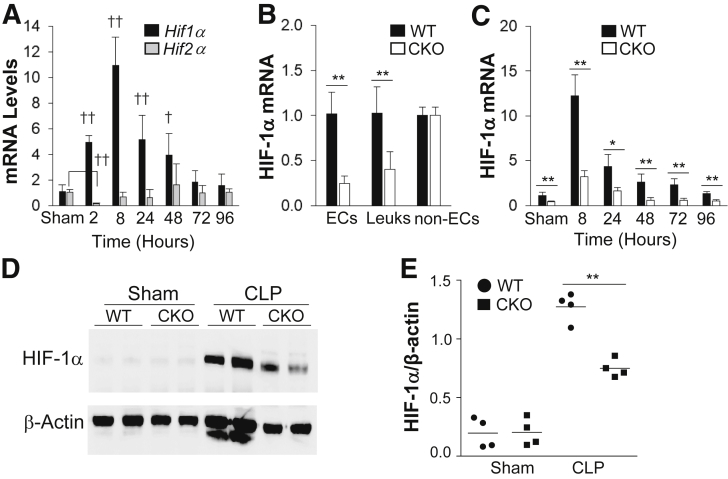
Figure 1.
HIF-1α rapidly induces mouse lung endothelial cells (ECs) after cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) challenge. A: Real-time quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis demonstrating rapid induction of HIF-1α, but not HIF-2α, expression in lungs of wild-type (WT) mice after CLP. HIF-2α expression is initially decreased at 2 hours after CLP and then returns to basal levels, whereas HIF-1α expression is markedly induced and peaks at 8 hours after CLP. B: HIF-1α mRNA expression in isolated lung ECs (CD45−/CD31+), leukocytes (Leuks; CD45+/CD31+), and non-ECs, including epithelial cells and fibroblasts (CD45−/CD31−), from WT and Hif1af/f/Tie2Cre+ (CKO) mouse lungs by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. C: RT-qPCR analysis demonstrating inhibited HIF-1α induction in Hif1af/f/Tie2Cre+ lungs after CLP challenge. D: Representative Western blot analysis demonstrating marked inhibition of HIF-1α protein expression in CKO mouse lungs at 8 hours after CLP compared with WT lungs. β-Actin was used as a loading control. E: Quantification of Western blot analysis band intensity using ImageJ software version 1.51a (NIH, Bethesda, MD; http://imagej.nih.gov/ij). Data are expressed as means ± SD (A–C) and means (E). n = 5 mice per group (A); n = 4 mice (B, demonstrating Tie2Cre-mediated Hif1a deletion in ECs and leukocytes, and C, per group). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 (t-test); †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01 compared with WT-sham (one-way analysis of variance with a Tukey's post hoc analysis for multiple-group comparisons and t-test for two-group comparison).