Figure 2.
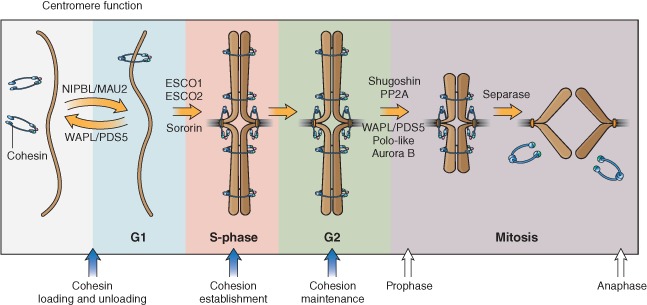
Schematic diagram showing cohesin regulation throughout the cell cycle. Cohesin (blue) is loaded onto chromosomes in telophase/G1 phase by the NIPBL–MAU2 heterodimer and requires the opening of the hinge domain of SMC1A and SMC3 for DNA entry. Cohesion establishment at S phase is facilitated by ESCO1/2‐dependent acetylation of the SMC3 head domain, making cohesin refractory to removal from chromatin by WAPL. Cohesion is then maintained by other proteins such as WAPL, PDS5, and Sororin. Cohesin can be removed in prophase in a separase‐independent manner from chromosome arms. This removal depends on PLK1 and WAPL/PDS5. Pericentromeric cohesion is protected by shugoshin and PP2A. At the onset of mitosis, pericentromeric cohesion is destroyed by proteolytic cleavage of RAD21 by separase and recycled for the next cell cycle. Recycling of the SMC3 subunit requires deacetylation by HDAC8.
