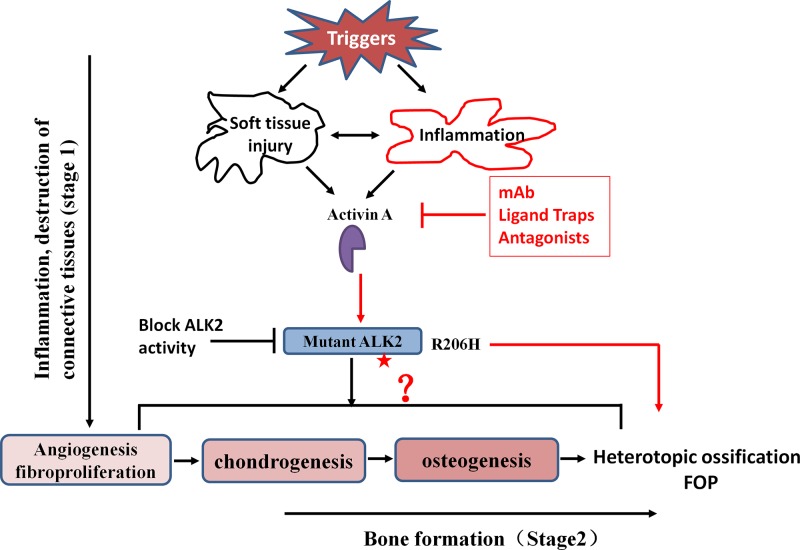
Figure 3. Schematic presentation of Activin A and its involvement in the formation of heterotopic bone in FOP.
HO formation involves inflammation and the destruction of connective tissues followed by bone formation. After various triggers, such as injury, abundant perivascular lymphocytes are present in damaged tissue. Activin A is secreted by the lymphocytes and induced by inflammation, then activates ALK2 R206H signaling as an osteogenic ligand. Some progenitor cells are recruited and differentiate into chondrocytes and osteoblasts, eventually forming heterotopic bones in soft tissues. However, the previous studies do not indicate the involvement of Activin A in the exact stages of HO formation. In addition, targets and strategies for the prevention and treatment of FOP presents : inhibition of Activin A and block mutant ALK2 activity. See the text for details. The star: classic mutation site of ALK2 R206H.