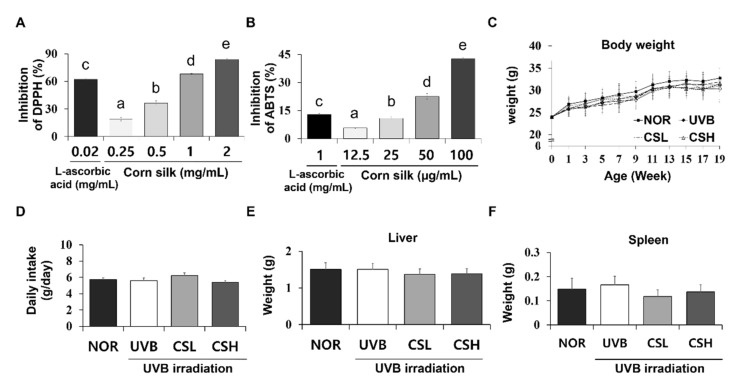
Figure 1.
DPPH and ABTS antioxidative assay of corn silk (CS) extracts and the general details of SKH-1 mice during the experiment. Antioxidative effects of CS extracts were determined by DPPH (A) and ABTS radical scavenging activity (B). For the assays, CS extracts at concentrations of 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 mg/mL and DPPH or ABTS solution were mixed at a ratio of 1:4 and 1:99. Body weight (C), food intake (D), liver weight (E), and spleen weight (F) of the mice were not significantly different across all groups (n = 8~10 per group) including normal control group (NOR), UVB-irradiated group (UVB), UVB-irradiated and low CS- (2 g/kg/day) treated group (CSL), and UVB-irradiated and high CS- (4 g/kg/day) treated group (CSH). Values are mean ± SD. The results were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s post-hoc test. Different lowercase letters over bars (a, b, c, d, e) represent significant statistical differences (p < 0.05).