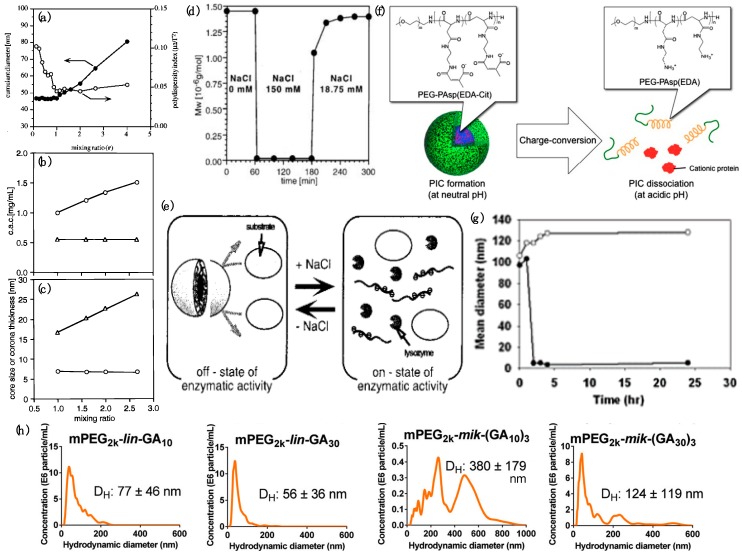
Figure 7.
(a–c) various physical attributes of lysozyme/PEG-b-P(Asp) micelles varying with mixing ratio r at lysozyme concentration 2.0 mg/mL. (a) cumulant diameter (filled circles) and the polydispersity index (open circles); (b) critical association concentration (c.a.c.) (circles: c.a.c. of total concentration (lysozyme + P(Asp) + PEG); triangles: c.a.c. converted to the concentration of charged segments (lysozyme+P(Asp)); (c) core size (circles) and corona thickness (triangles) all changing with the mixing ratio r. (a) reprinted with permission from Ref. [58]. Copyright 1999 American Chemical Society. (b,c) adapted with permission from Ref. [57]. Copyright 1998 American Chemical Society; (d) fast and reversible dissociation and formation of protein–PE micelles upon exposure to high and low NaCl concentrations, respectively; (e) schematic illustration of the concomitant regulation of enzymatic activity of lysozymes upon incorporation and release from micelles; (d,e) adapted with permission from Ref. [59]. Copyright 1999 American Chemical Society; (f) schematic illustration of the stable micelle comprising PEG-b-pAsp(EDA-Cit) at neutral pH and the charge-conversion of block copolymer leading to micellar dissociation along with protein release at acidic pH. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [133]; (g) size of the protein/bPE micelles of PEG-b-pAsp(EDA-Cit) varying with time. Reprinted with permission from [136]. Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society; (h) micelle size distribution of mPEG2k-lin-GA10, mPEG2k-lin-GA30, mPEG2k-mik-(GA10)3 and mPEG2k-mik-(GA30)3-derived complexes with lysozyme at charge ratio 1.0. Reproduced from Ref. [137] by permission of the Royal Society of Chemistry.