Figure 3.
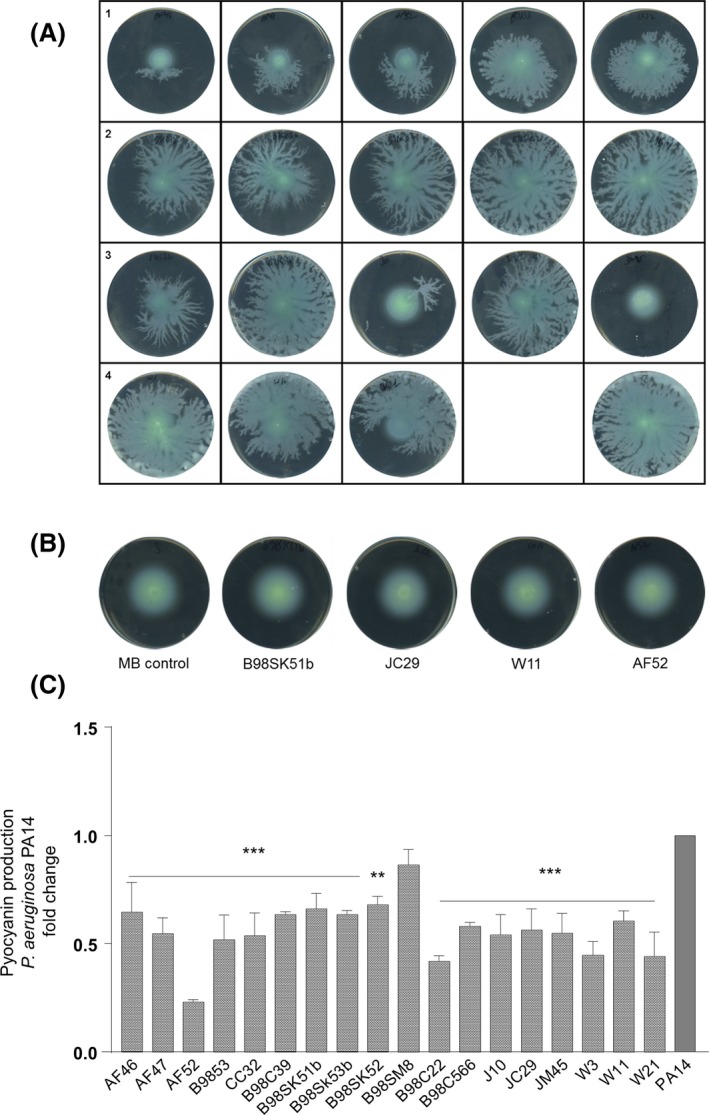
QQ marine bacterial supernatants impair different virulence phenotypes of P. aeruginosa PA14.
A. Impact of marine bacterial supernatants on PA14 swarming motility. Row 1, from left to right: Bacillus sp. AF46, AF47, AF52, B9853 and CC32. Row 2, from left to right: Pseudomomas sp. B98C39, B98SK51, B98SK53B, B98SK52 and B98SM8. Row 3, from left to right: Psychrobacter sp. B98C22, Staphylococcus sp. B98C566, Pseudoalteromonas sp J10 and JC29 and Paracoccus sp. JM45. Row 4, from left to right: Pseudoalteromonas sp. W3, W11 and W21. The untreated MB control is presented on the far right of this row.
B. Impact of marine bacterial supernatants on PA14 swimming motility.
C. Impact of marine bacterial supernatant on PA14 pyocyanin production.
Data presented are normalized to the PA14 control and are the mean (±SEM) of at three independent biological replicates. In each case, the individual replicates of the untreated control are normalized to the mean. Statistical analysis was performed using one‐way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni testing (**P ≤ 0.005, ***P ≤ 0.001).
