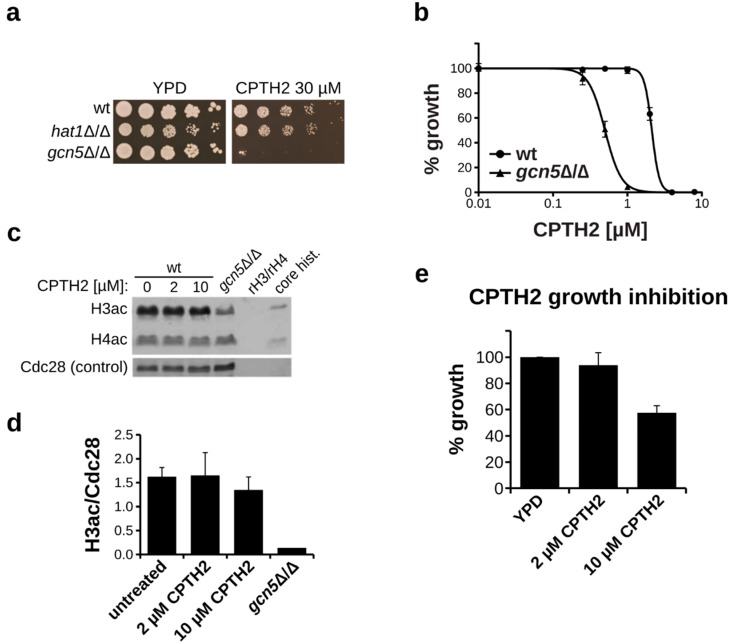
Figure 2.
CPTH2 inhibits C. albicans independently of Gcn5. (a) Spot dilution assay of the indicated C. albicans strains on YPD plates. The gcn5Δ/Δ strain shows increased sensitivity to CPTH2. (b) Liquid growth inhibition assay in YPD medium. C. albicans wt and gcn5Δ/Δ cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of CPTH2 for 24 h prior to OD600 measurement. (c) Immunoblot of histone H3 and H4 acetylation upon treatment with CPTH2. Cells were treated with the indicated concentration of CPTH2 for 4 h prior to SDS-Page analysis followed by immunoblotting with an anti-acetyl lysine antibody. Cdc28 served as loading control. Unacetylated recombinant histones (rH3, rH4) and chicken core histones were used as negative and controls, respectively. (d) Quantification of histone H3 acetylation levels upon CPTH2 treatment using immunoblotting as described above (c). (e) Growth inhibition by CPTH2 of C. albicans cultures used for immunoblotting described in (c). OD600 was measured after 4 hours of treatment. (b,d,e) Data shown are mean ± sd of three biological replicates.