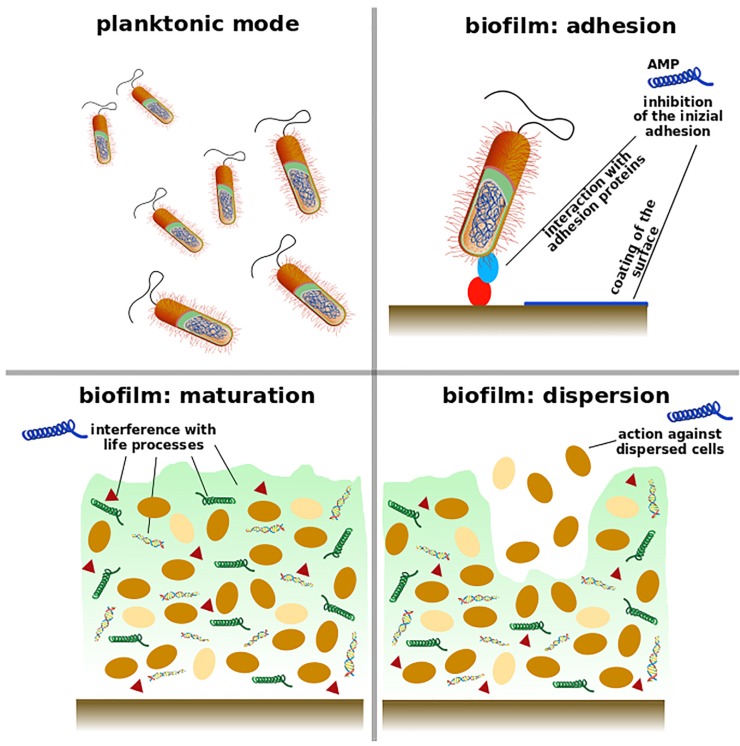
Figure 1.
Biofilms develop in three phases: initial adhesion, maturation, and dispersion. A good anti-biofilm agent (blue peptide) can be involved in all the biofilm phases. AMPs may inhibit the accumulation of bacteria on the surface by interacting with their adhesion proteins (red and light blue) or coating the surface to protect from bacterial attack. Antimicrobial peptides can display an action against bacteria in their active state in the biofilm (brown); they can also defeat bacteria in the persisters models (yellow) or interfere with life processes such as synthesis of EPS (light green matrix), signaling compounds (triangle), extracellular DNA, and proteins (green helix).