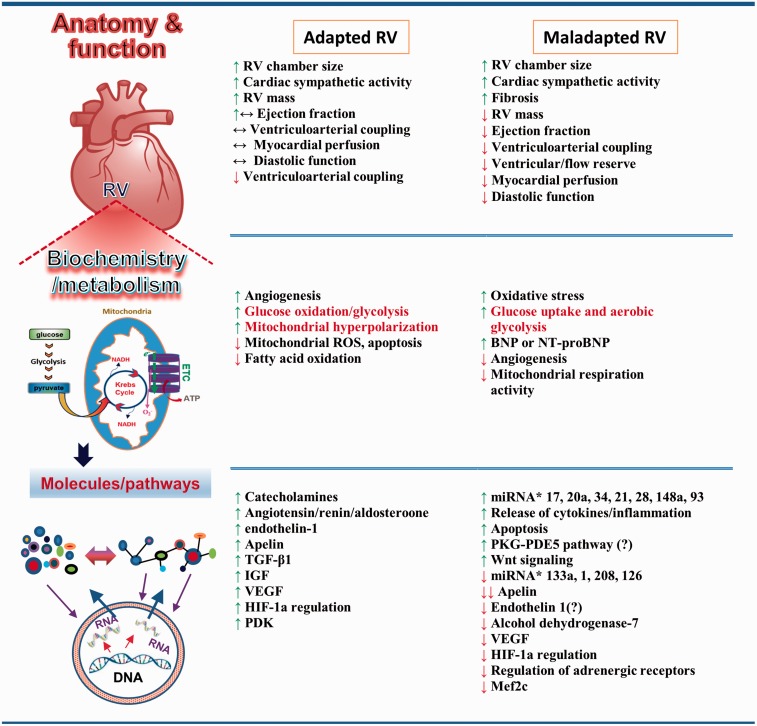
Fig. 4.
Features of RV adaptation and RVF. RV adaptation and RVF manifest at different levels of organization. At the organ level, RV adaptation is associated with RVH and maintained function. RVF presents as alterations in anatomy and function. At the cellular level, changes in metabolism and biochemistry occur in both adapted RV and RVF. Some metabolic mediators are found in both adapted and maladapted RV, and their roles in promoting each are controversial. At the molecular level, metabolites, molecules, proteins, and mediators of signaling pathways are altered or modified in adapted RV and RVF. New signaling pathways and mediators have been identified in RVF. BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; ETC, electron transport chain; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; miRNA, microRNA; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide; PDE5, phosphodiesterase-5; PDK, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; PKG, protein kinase G; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor beta 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.6,73,94,98,124,125