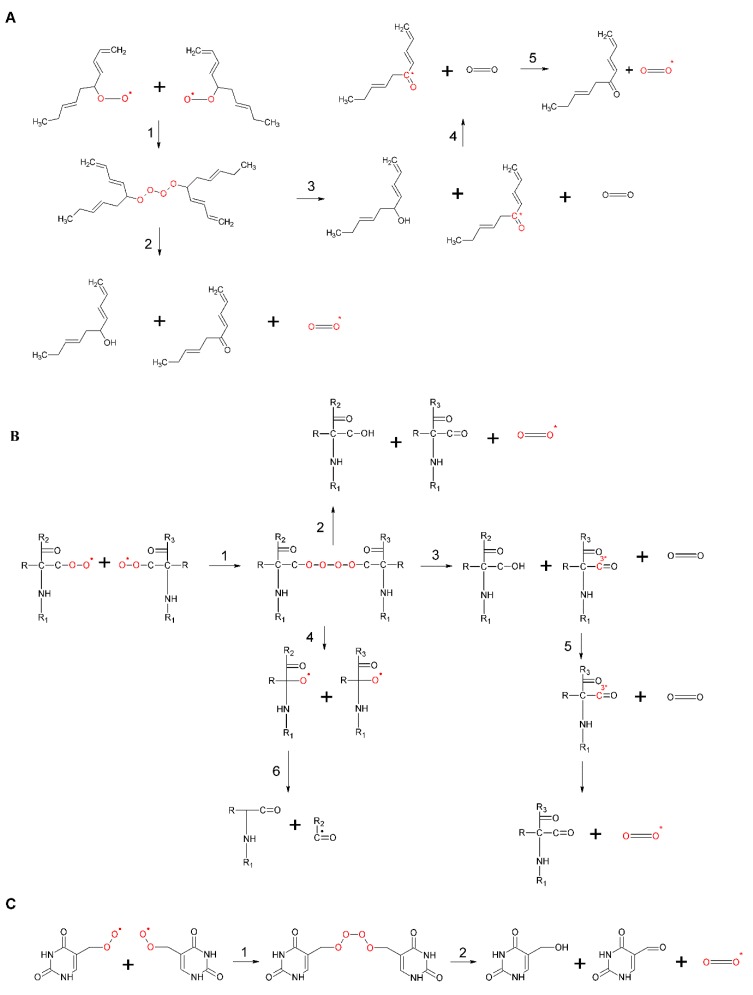
Figure 6.
Formation of ROOOOR by the recombination of two lipid ROO• (A), protein ROO• (B), and DNA ROO• (C). In (A–C), the recombination of two ROO• results in the formation of unstable ROOH (reaction 1). ROOH can decompose either to ground carbonyl, 1O2 and ROH (reaction 2) or to 3R=O*, molecular oxygen and ROH (reaction 3). The triplet-singlet energy transfer from 3R=O* to molecular oxygen causes the formation of 1O2 (reactions 4). In (B), ROOH can decompose into two RO• in the presence of reducing agents (reaction 5).