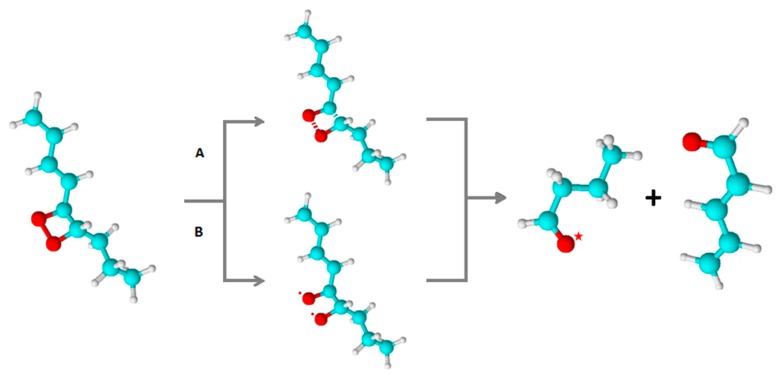
Figure 8.
Thermal decomposition of 1,2-dioxetane by concerted (A) and diradical (B) mechanisms. In (A), the concerted mechanism involves the simultaneous cleavage of oxygen-oxygen and carbon-carbon bonds. In (B), diradical mechanism contains the cleavage of the oxygen-oxygen bond, resulting in the formation of diradical, followed by the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond. Both mechanisms result in the formation of triplet exited carbonyl and ground state carbonyl.