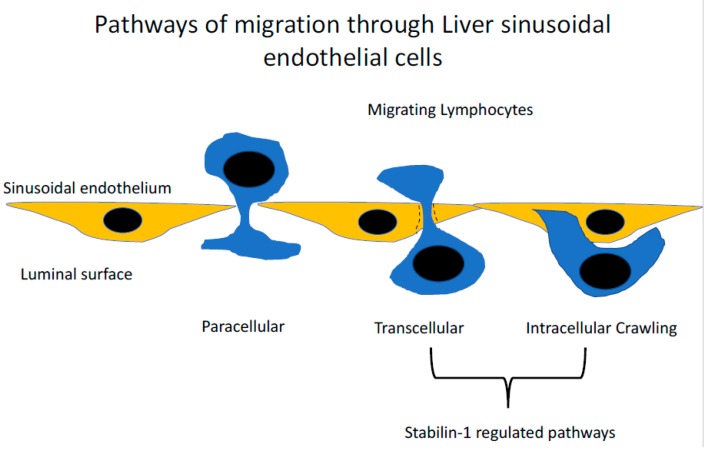
Figure 3.
The routes taken by lymphocytes during transendothelial migration. Detailed analysis of the last step of the adhesion cascade where lymphocytes cross the endothelial barrier have demonstrated that several routes can be taken. The conventional route is the paracellular route, where lymphocytes migrate directly between endothelial cellular junctions. The second route, which appears to occur in the liver at a high frequency, is the migration of lymphocytes directly through the body of the cell, termed the transcellular migration. This route of migration has been described in other microvascular beds including the lymphatics and bone marrow. An additional novel route has also been described where lymphocytes invade into the body of the endothelial cell and then migrate directly into the adjacent endothelial cell termed ‘intracellular crawling’. Stabilin-1 has been shown to contribute to both transcellular migration and intracellular crawling.