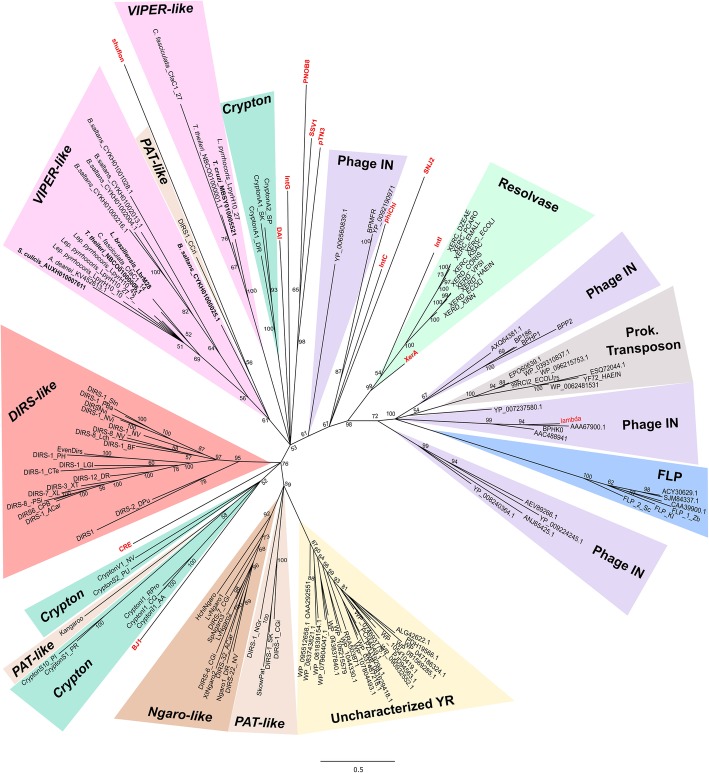
Fig. 6.
Phylogenetic relationships of YR family proteins. Unrooted BA tree (mixed model + G, 157 aa) based on the YR amino acid sequences from DIRS retrotransposons (DIRS-like, PAT-like, Ngaro-like, and VIPER-like) along with other YR family proteins: resolvase [site-specific recombinases involved in chromosome dimer resolution in archaea (XerA) and bacteria (XerC/D)], FLP (yeast Flp-like flippases), phage integrase, prokaryote transposons, Crypton, uncharacterized YR (proteins retrieve by blastp searches). YR sequences from the distinct groups shown by Wang et al. (2018) are in red: shufflon (shufflon-specific DNA recombinases); DAI (dusA-associated integrases); phage integrases; IntC (integrases from integrative and conjugative elements); IntI (integron integrases); IntG (genomic island integrases); XerA (site-specific recombinases involved in chromosome dimer resolution in archaea), Cre (phage P1-like recombinases); archaeal SSV-type, pNOB8-type and pTN3-type integrases; and integrases encoded by haloarchaeal SNJ2, BJ1-like and phiCh1-like viruses. Possible encoding copies of VIPER and TATE are highlighted in bold. Posterior probability values are indicated above the nodes, and clades with support less than 50% were collapsed; bootstrap values from ML analysis are presented in blue below the nodes (only values above 50)