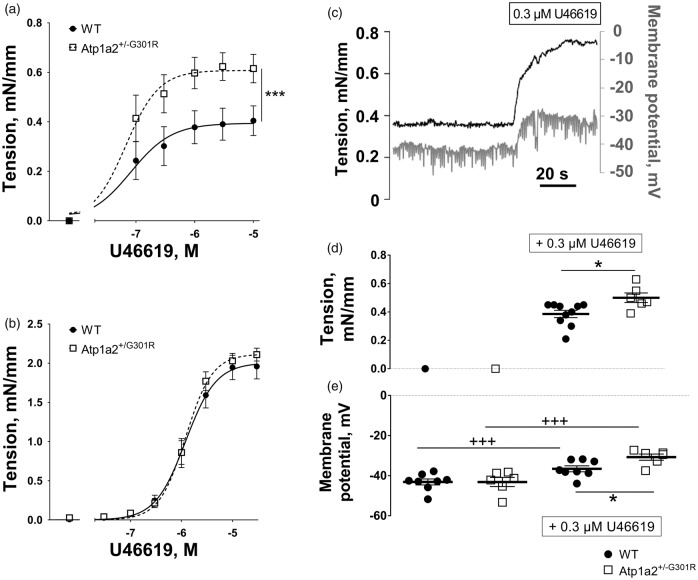
Figure 3.
Middle cerebral but not small mesenteric arteries from Atp1a2+/−G301R mice had increased agonist-induced constriction and depolarization in comparison with WT. Concentration-response curves to U46619 of middle cerebral arteries (a) from Atp1a2+/−G301R (n = 7) and WT mice (n = 9). F test indicated a significant difference between experimental groups (***, P < 0.05). No difference in U46619-induced constriction was seen between mesenteric small arteries from Atp1a2+/−G301R and WT mice (b; n = 6). A representative simultaneous recording of wall tension and membrane potential in WT middle cerebral artery stimulated with U46619 (c). Wall tension (d) and membrane potentials (e) under resting conditions and after 0.3 µM U46619 stimulation of middle cerebral arteries from Atp1a2+/−G301R (n = 6) and WT mice (n = 8). The experimental protocol is similar to data shown in c. *, P < 0.05, comparison between Atp1a2+/-G301R and WT groups; +++, P < 0.001, the effect of U46619 (two-way ANOVA).