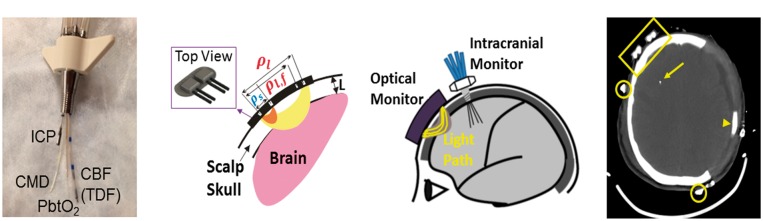
Figure 1.
(a) Picture of quad lumen bolt with invasive probes. (b) Schematic of NNOM sensor that probes the head with: (1) TR-NIRS measurements at long (ρl = 3.2 cm) and short (ρs = 0.7 cm) source-detector separations to derive cerebral StO2 and OEF; and (2) DCS measurements at long (ρl,f = 2.5 cm) and short (ρs = 0.7 cm) source-detector separations to derive a CBF index (see text). (c) Configuration of concurrent non-invasive and invasive intracranial monitoring probes. (d) Anatomical CT scan showing position of NNOM sensor on the scalp (encompassed by yellow rectangle) and the tip of an invasive probe (yellow arrow). The patient’s skull was surgically removed from the left side to treat cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension. Arrowhead points to subdural drain, and open circles mark positions of EEG electrodes.