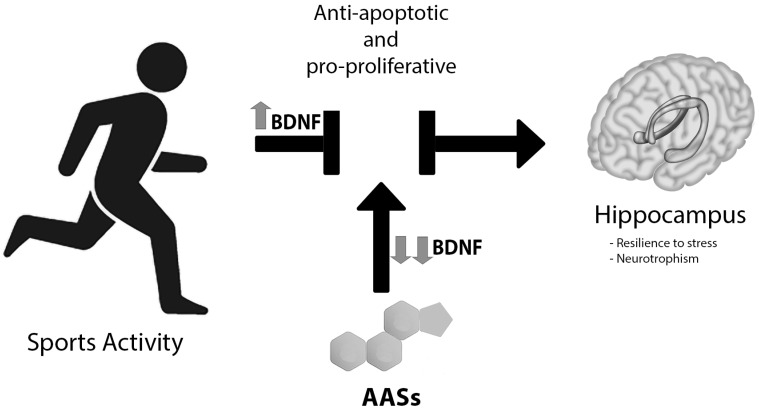
Figure 3.
AASs vs. sport exercise: The latter determines important anti-apoptotic and pro-proliferative functions on the hippocampus, implicated in anxiolytic control. AAS consumption blocked this effect, likely via brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), mRNA expression is inversely dependent on AAS use. Moreover, exercise seems to not be capable of repairing hippocampal AAS-induced damage. The result is a significant lowering of the hippocampal levels of BDNF, reducing adaptability to stress and neurotrophism.