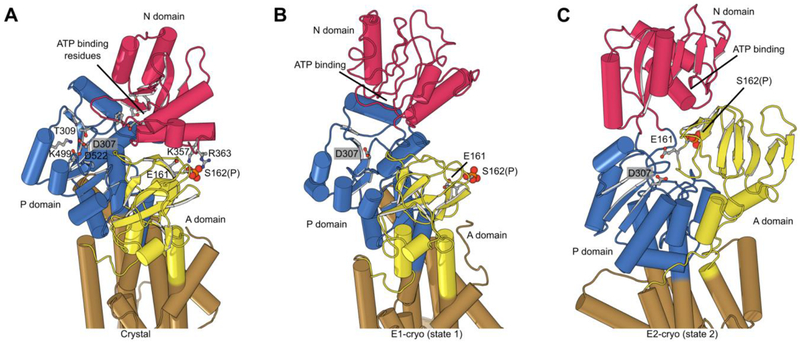
Figure 6:
Phosphorylation and structural environment of Ser162. This residue is part of the conserved TGES motif in the A domain (yellow), which occupies different configurations in the three structures. (A) Crystal structure which represents the E1 enzymatic state. (B) State 1 structure from cryo-EM which also represents the E1 state. (C) State 2 from cryo-EM which represents the E2 state. The phosphor-serine, S162(P), mediates a salt bridge with two non-conserved residues in the N domain (red) in the X-ray structure. The A domain is known to be highly mobile and although its resolution in cryo-EM maps was not sufficient to see the phosphate, the juxtaposition of A and N domains in these two structures indicated that the salt bridge could not be formed. In state 2, E161 is seen approaching the catalytic aspartate (D307) in the P-domain (blue), which reflects its role in hydrolysis of the phosphoenzyme in the E2 state.