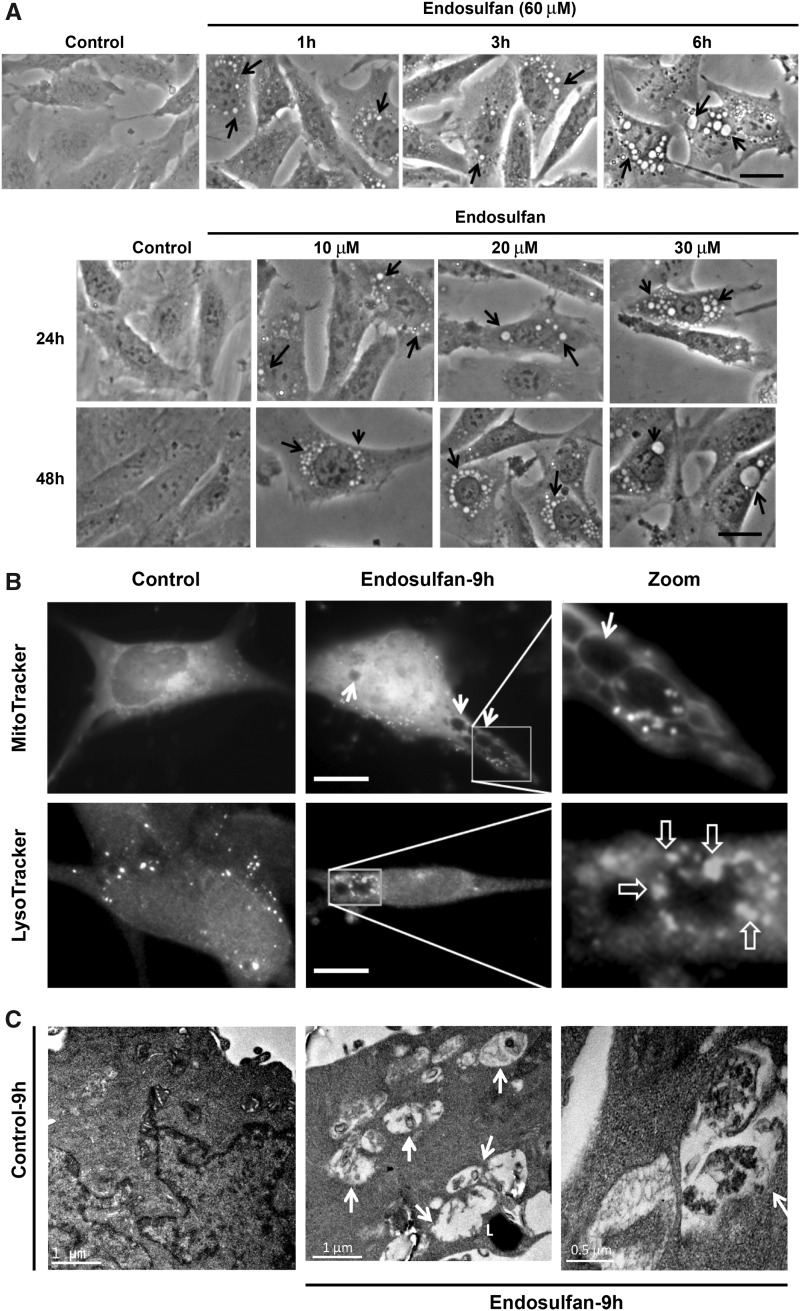
Figure 2.
Endosulfan-induced autophagy in N27 dopaminergic neuronal cells. (A) Autophagic vacuoles were examined by phase-contrast microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) MitoTracker and LysoTracker fluorescent staining imaged after 9-h exposure to endosulfan. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Representative transmission electron microscopy images depicting the ultrastructure of cells treated with 60 μM endosulfan for 9 h. Arrows, autophagic vacuoles. Arrowheads, autophagosome assembly (cargo capturing). Scale bars 0.5 and 1 μm. (D) Cells were transfected with one of the GFP-LC3 fusion constructs (wild type or mutant ΔG). Puncta formed in cells transfected with GFP-LC3 cDNA and treated by endosulfan for 3 and 6 h. GFP-LC3 dots were not observed when cells were transfected with GFP-LC3-ΔG cDNA. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Immunoblot analyses of accumulating LC3-II protein in cells treated with 60 µM endosulfan; β-actin expression was used as an equal loading control. (F) MDC assay was performed in control or endosulfan-exposed cells. ***, p < .001 indicates significant differences between endosulfan-treated groups and vehicle-treated control cells.