Figure 3.
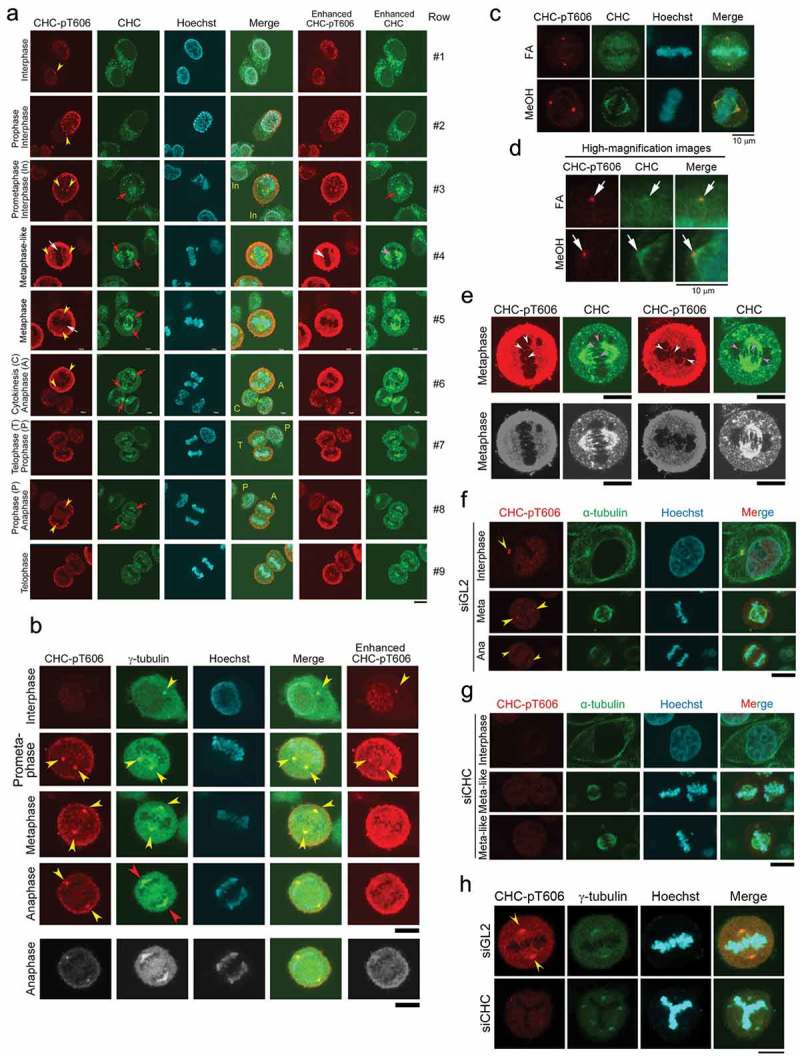
CHC-pT606 signals are observed in the nucleus during interphase and at the centrosome during M phase. (A) Subcellular localizations of CHC-pT606 and CHC during the cell cycle. IF analysis of HeLa S3 cells was performed using an anti-CHC-pT606 polyclonal Ab and an anti-CHC monoclonal Ab. Typical IF images at interphase and M phase are shown at different stages of the cell cycle. Contrast-enhanced images of CHC-pT606 and CHC signals are also shown in the rightmost panels. Yellow arrowheads and red arrows indicate the putative localizations of these signals at the centrosome and mitotic spindle, respectively. White arrows at metaphase indicate the localization of CHC-pT606 signals at mitotic spindle. (B) Co-localization of CHC-pT606 with γ-tubulin suggests that it localized at the centrosome. (C) Co-localization of CHC-pT606 with a part of CHC at the centrosomes in mitotic HeLa S3 cells fixed with formaldehyde (FA) and methanol (MeOH). DNA was counter-stained with Hoechst33258 to detect chromatin. (D) High-magnification images of the cells shown in C highlight the partial co-localizations of CHC-pT606 and CHC (white arrows) at asters during metaphase. (E) Enlarged images show that CHC-pT606 (white arrowheads) and CHC (pink arrowheads) signals co-localize primarily at the tips of mitotic spindle MTs. (F–H) Typical IF images of cells during interphase and M phase following siRNA-mediated knockdown using siGL2 (F, top panel in H) or siCHC (G, bottom panel in H). DNA was counter-stained with Hoechst33258 to detect chromatin. Yellow arrowheads indicate localization at the centrosome. Bars, 10 µm.
