Figure 2.
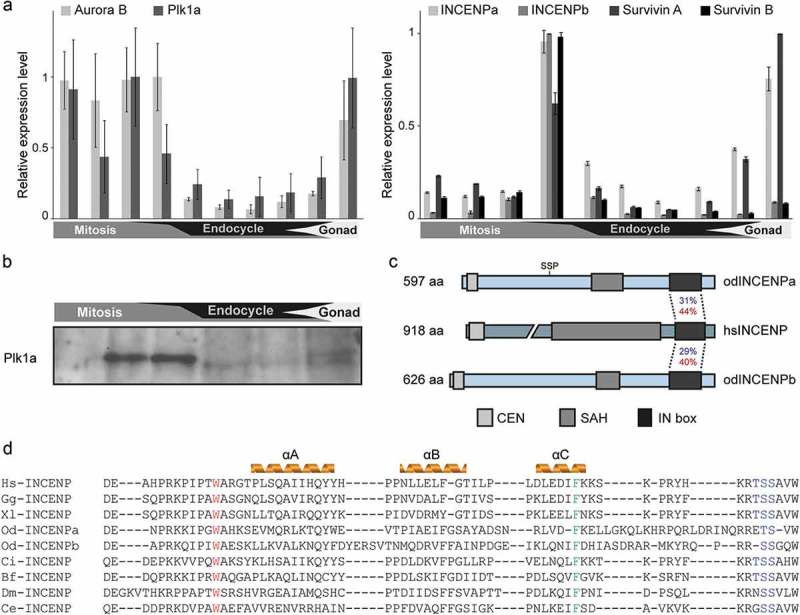
Temporal expression pattern of the CPC components and Plk1a during O. dioica development. (a) Developmental expression analysis of core CPC components and Plk1a. Aurora B and Plk1a (left), and two coexisting INCENP and Survivin paralogs (right), were highly expressed during mitotic proliferation and gonad development. Paired histogram bars correspond to the following developmental stages from left to right: oocytes, 2–8 cells, 1 hpf, hatching, metamorphosis, Day 2, Day 3, Day 4, Day 5 and Day 6. Mean RT-qPCR values normalized to EF1β transcripts (n = 3) are shown with SE. (b) Plk1a protein was enriched during mitotic development as determined by western blot using odPlk1a antibody. Equal amounts of whole animal lysates from various stages were loaded. (c) Domain comparison of Homo sapiens and O. dioica INCENP homologs. N terminal CEN, single α-helix (SAH) and C terminal IN box domains are indicated. Identities (blue) and similarities (red) between O. dioica INCENP paralog IN boxes and the single human ortholog IN box are shown. The CDK1 consensus phosphorylation site (SS209P) is positioned on INCENPa and is absent in INCENPb. (d) Sequence alignment of the INCENP IN box with predicted secondary structure in several model species. W801 (Xenopus numbering), involved in Aurora B interaction, is marked in red and F837, involved in Aurora B activation, is marked in green. Aurora B phosphorylation sites “TSS” are marked in blue. Hs, Homo sapiens; Gg, Gallus gallus; Xl, Xenopus laevis; Od, Oikopleura dioica; Ci, Ciona intestinalis; Bf, Branchiostoma floridae; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans.
