Figure 11.
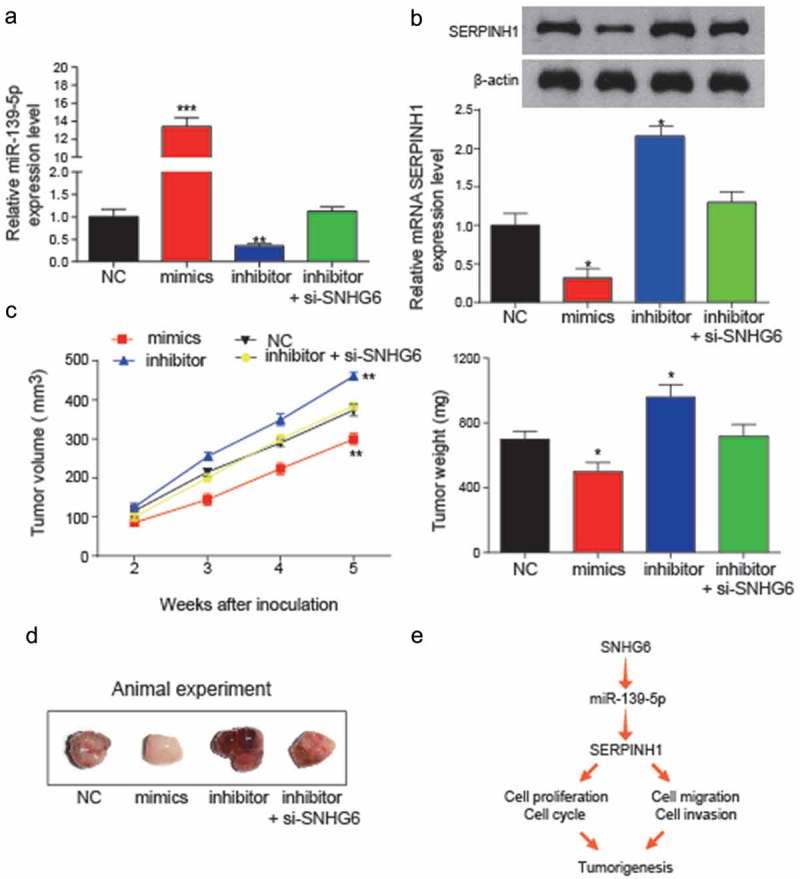
In vivo assay was used to validate the effects of miR-139-5p and SNHG6 on tumor growth. (a) Expression levels of miR-139-5p in transfection groups were analyzed to verify the transfection efficiency (**P< 0.01, compared with NC group). (b) Relative expression levels of SERPINH1 in transfection groups were detected by qRT-PCR and western blot. The inhibition of miR-139-5p could significantly induce the expression level of SERPINH1. (*P< 0.05, compared with NC group) (c) miR-139-5p inhibited HCC cell growth in vivo. Tumor growth curve of NC, mimics, miR-139-5p inhibitor, miR-139-5p inhibitor + si-SNHG6 transfected HepG2 cells in nude mice was shown as mean ± SD (left panel). The changes in tumor weight among different inoculation groups (right panel). (*P< 0.05, ** P< 0.01, compared to NC group) (d) Images of the tumors induced by NC, mimics, miR-139-5p inhibitor or miR-139-5p inhibitor+si-SNHG6 transfected were shown. (e) The conclusion of the regulation relationship among SNHG6, miR-139-5p and SERPINH1, and their regulation might influence the cell cycle, cell proliferation, cell migration and invasion and further influence the HCC tumorigenesis. Every experiment was performed for 3 times at least.
