Fig. 6. A mutation near the pbp4 gene appears in later outbreak strains of E. faecalis.
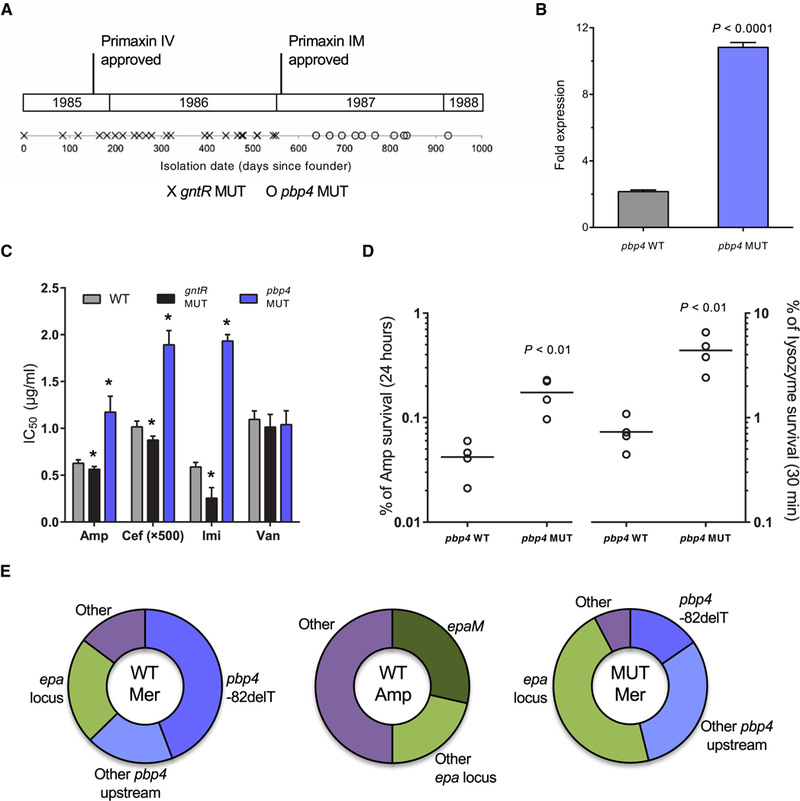
A mutation near the gene encoding pbp4 appeared in later strains most likely in response to pressure from carbapenem treatment. (A) Timeline for outbreak strains containing mutations in gntR (gntR MUT) or a mutation 82 nucleotides upstream of pbp4 (pbp4 MUT). Approval dates for intravenous (IV) and intramuscular (IM) formulations of Primaxin (imipenem/cilastatin), the first carbapenem antibiotic, are shown. (B) Fold mRNA expression of pbp4 in wild-type (WT) and MUT E. faecalis outbreak strains. (C) The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) values after treatment of WT, gntR MUT, and pbp4 MUT strains with ampicillin (Amp), ceftriaxone (Cef), imipenem (Imi), and vancomycin (Van). *P < 0.005 calculated with a two-tailed t test of each MUT strain relative to WT. (D) Survival of pbp4 WT and MUT strains after treatment for 24 hours with a lethal dose (10x WT MIC) of Amp or for 30 min with lysozyme (10 mg/ml). CFU per milliliter were determined at the beginning and at the end of the assay, and survival was calculated as a percentage of the starting CFU per milliliter. Data points represent independent biological replicates, and horizontal lines indicate mean values. (E) Distribution of mutations among antibiotic-resistant mutants on WT or gntR MUT strain backgrounds that were selected on meropenem (Mer) or Amp in vitro. After confirmation of resistant phenotypes, mutants were genotyped by PCR and Sanger sequencing or by genome sequencing. Bar charts in (B) and (C) show mean values with error bars indicating the SD of at least three biological replicates. All P values were calculated with a two-tailed t test.
