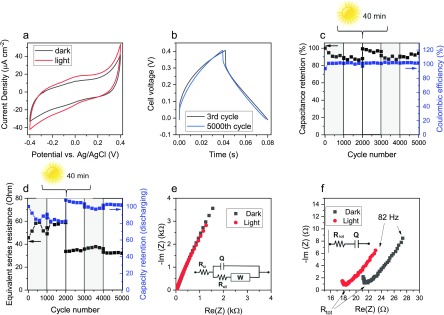
Figure 2.
Electrochemical characterization of DHI-melanin in the aqueous buffer of 0.25 M NaCH3COO (pH 5) in both dark and light conditions. (a) Cyclic voltammetry at the scan rate of 5 mV s–1. (b) Galvanostatic charge and discharge of the DHI-melanin supercapacitor at 5 A g–1. (c) Capacitance rated to the initial value and Coulombic efficiency for 5000 cycles of galvanostatic charge and discharge. (d) Equivalent series resistance and capacity rated to the initial value for 5000 cycles of galvanostatic charge and discharge. Protocol of acquisition: dark → light → 40 min irradiation (without current or electrochemical potential applied) → light → dark → light, each for 1000 cycles. Gray rectangles indicate the dark conditions. (e) Nyquist plot in the frequency range 105 and 10–1 Hz. Inset: corresponding equivalent circuit. (f) Zoomed Nyquist plot in the frequency range 105–82 Hz. Inset: corresponding simplified simulated circuit. Cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance experiments are performed in a three-electrode cell (i.e., they describe the single-electrode behavior), whereas galvanostatic charge and discharge characterizations refer to the full supercapacitor cell (two electrodes) (Scheme S1).