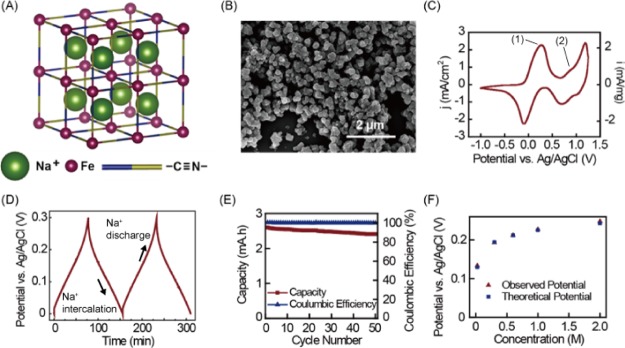
Figure 2.
(A) Crystal structure of PB showing the open-framework structure, allowing insertion and extraction of Na+; (B) scanning electron microscopy image of the PB electrode; (C) cyclic voltammetry of the PB electrode in a 0.6 M NaCl solution; (D) galvanostatic cycle of the PB electrode in a 0.6 M NaCl solution; (E) cycling performance of the PB electrode, showing the coulombic efficiency and discharge capacity over 50 cycles; (F) PB electrode potential changed with different NaCl concentrations (0.024, 0.3, 0.6, 1, and 2 M).