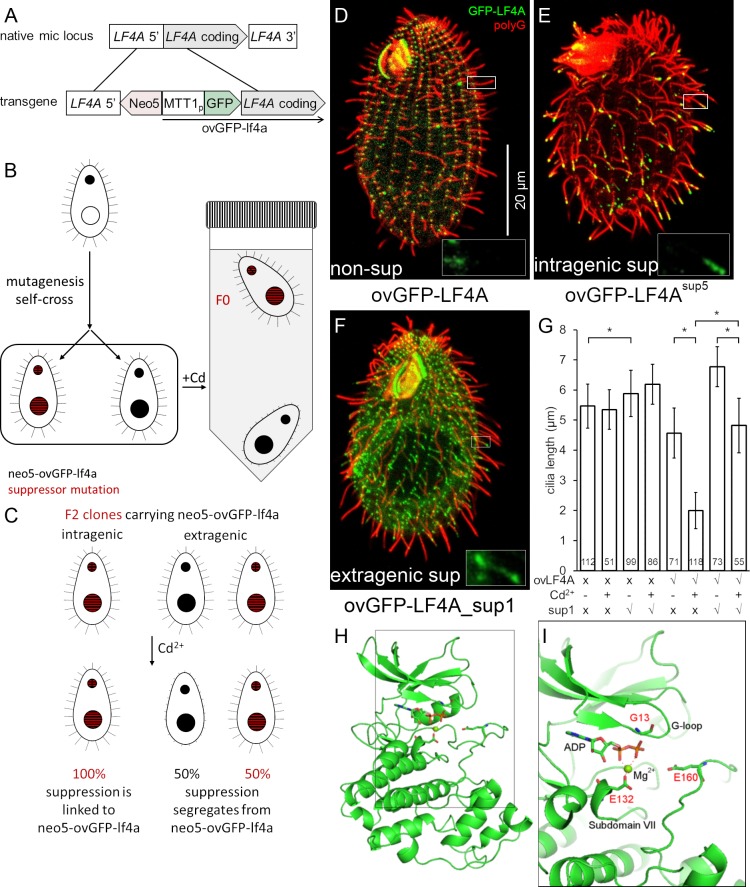
Fig 4. Isolation of intragenic and extragenic suppressors of GFP-LF4A overexpression.
(A-C) The pipeline used for identification of intragenic and extragenic suppressors of overexpression of GFP-LF4A. (A) The structure of the transgene that was placed in the micronucleus. The transgene uses MTT1 promoter to express GFP-LF4A. A neo5 cassette is closely linked. The transgene replaces the endogenous LF4A. (B) An outline of the procedure for generating suppressors. A heterokaryon with the ovGFP-lf4a transgene in the micronucleus (solid black) was subjected to mutagenesis and a self-fertilizing cross. The homozygous progeny was selected based on paromomycin resistance conferred by neo5 and some progeny clones may carry a suppressor mutation (red stripes). The progeny cells were treated with Cd2+ in tubes kept in vertical position. The progeny clones that lack a suppressor mutation shorten cilia and sink to the tube bottom. The suppressors (F0) remain motile and accumulate near the top of the tube due to negative gravitaxis. (C) The principle of testing whether the suppression is intra- or extragenic (for details see S3 Fig). The F1 clones were subjected to a self-cross and the pm-r F2 progeny clones were isolated. An intragenic suppressor gives pm-r F2 progeny clones that are 100% motile (suppressed), as the suppression is linked to the transgene. An extragenic suppressor generates F2 pm-r clones that are either suppressed (motile) or not (paralyzed). (D-F) Cells that were exposed for 6 hours to Cd2+ to induce GFP-LF4A, subjected to immunofluorescence to reveal GFP (green) and polyG tubulin (red). Insets show the GFP-LF4A signal alone in examples of cilia at a higher magnification. (D) A non-mutagenized non-suppressed cell; GFP-LF4A is enriched at the bases of cilia. (E) An intragenic suppressor cell (SUP5); GFP-LF4A is enriched at the tips of both oral and locomotory cilia. (F) An extragenic suppressor cell (SUP1); GFP-LF4A is prominent at the bases, at the distal ends and along the ciliary shafts in short (presumably assembling) cilia. (G) The locomotory cilia length of F2 clones of four genotypes without and with 6 hours Cd2+ treatment. Sample sizes (number of cilia measured) are indicated, asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference (one way Anova p<0.01), error bars indicate SDs. (H) A 3D predicted structure of the kinase domain of LF4A based on homology-directed modeling using CDK of Cryptosporidium (Chain A of PDB 3NIZ) as template. (I) A zoomed-in view of a region of the structure showing three locations of substitutions (shown as sticks) found in the intragenic suppressors sup3 (E132K), sup4 (G13S) and sup5 (E160K).