Figure 8. Generation of MAHDR-Taar1+/+ knock-in and MAHDR-Taar1m1J/m1J control mice, and genotyping of Taar1 and Oprm1.
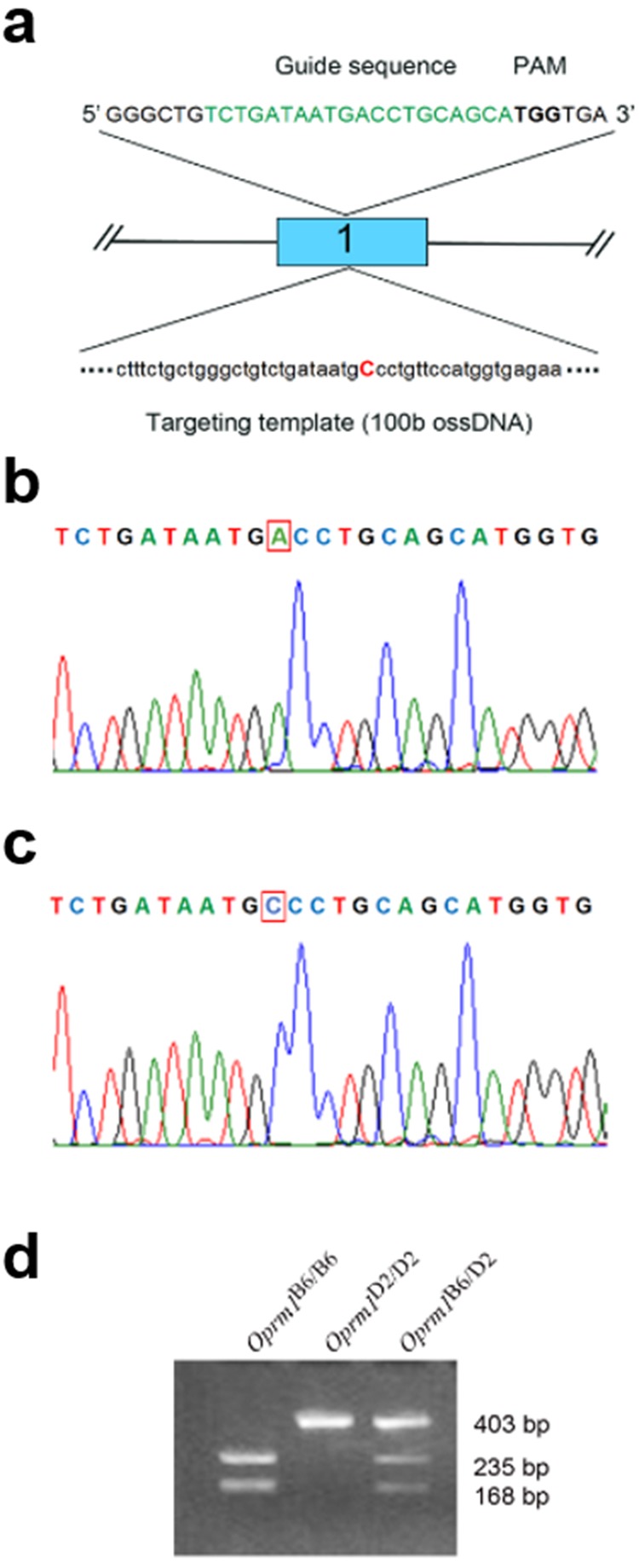
(a) Strategy for insertion of a point mutation into mouse Taar1 exon 1. The guide sequence is indicated in green text and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) is indicated by bold black text. The targeting template is indicated in black text, except for the single base pair to be inserted during the CRISPR-Cas9 process, which is indicated in red text. (b) A sequencing chromatograph of a homozygous Taar1m1J/m1J mouse that is representative of all MAHDR mice. The red box indicates the single nucleotide targeted for replacement during the CRISPR-Cas9 process. (c) A sequencing chromatograph of a homozygous MAHDR-Taar1+/+ edited knock-in mouse. The nucleotide that was successfully inserted during the CRISPR-Cas9 procedure is indicated by a red square. (d) An agarose genotyping gel example of Oprm1 genotypes for Oprm1B6/B6, Oprm1D2/D2 and Oprm1B6/D2 (from a B6 x D2 cross). All BXD mice were either homozygous Oprm1B6/B6 or Oprm1D2/D2, as well as homozygous for one or the other Taar1 allele. BXD, C57BL/6J (B6) x DBA2/J (D2); Oprm1, mu-opioid receptor gene; Oprm1B6/B6, homozygous for B6 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1D2/D2, homozygous for D2 Oprm1 allele; Oprm1B6/D2, heterozygous for B6 and D2 Oprm1 alleles; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif; Taar1, trace amine-associated receptor 1 gene; Taar1+/+, homozygous for reference Taar1+ allele; Taar1m1J/m1J, homozygous for mutant Taar1m1J allele.
