Figure 3.
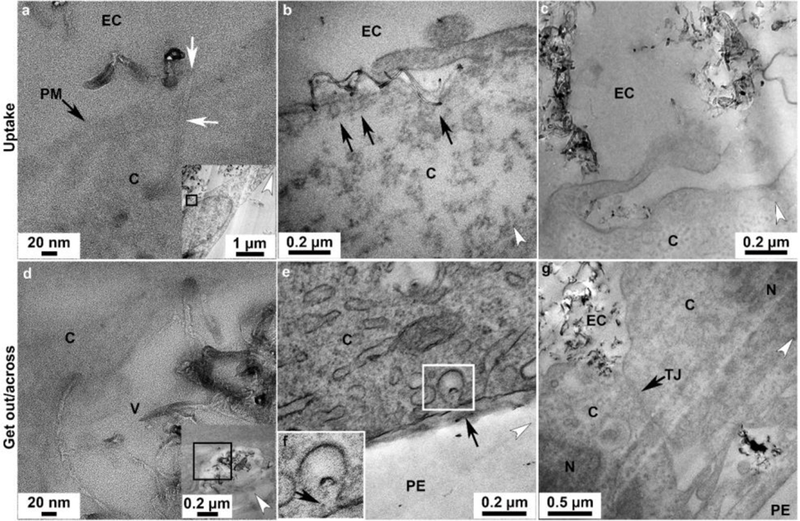
Transport pathways of p(4VP)-MWCNTs across TT1 monolayers. Similar trends of the uptake and transport were observed with TT1 cells exposed to 300 and 700nm p(4VP)-MWCNTs (see also in Figure 4). For the uptake: (a) HR-TEM image of a 700nm p(4VP)-MWCNTs (white arrows) inserted into the plasma membrane, PM (black arrow); panel a is taken from the boxed region in the inset panel showing the low magnification image of a. (b) Small aggregates of p(4VP)-MWCNTs activated the endocytic cups (arrows in b) prior to uptake by endocytosis. (c) Large aggregated 300nm p(4VP)-MWCNTs were taken up via macropinocytosis. (d) TEM imaging showed that 700nm p(4VP)-MWCNTs penetrated through a vesicle membrane (the insert figure shows the low magnification image of d). (e), Individual 300nm p(4VP)-MWCNTs were possibly released out from the vesicle via exocytosis at cell basal side (arrows in f). (f) The high magnification of the square in e. (g) The 700nm p(4VP)-MWCNTs were observed above and below the cell tight junction (TJ; arrow in h). EC, N, V, C, TJ and PE denote extracellular region, cell nucleus, vesicle, cytosol, tight junction and polyester membrane support, respectively. The white arrow heads indicate the knife marks and show the cutting direction.
