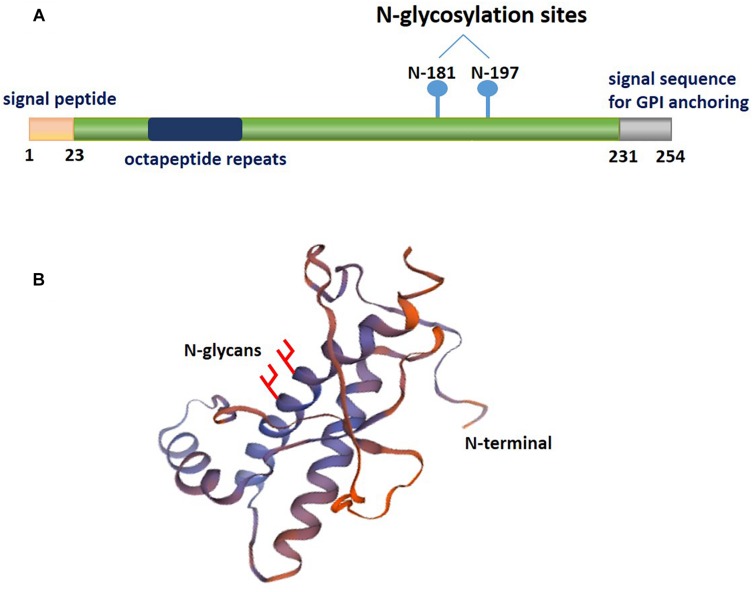
FIGURE 1.
A schematic illustrating the posttranslational modifications of PrPC. The relative size and localization of N-glycans in a schematic representation of the structural domains of PrPC. (A) The structure of PrPC can be divided into two distinct domains: a disordered N-terminal domain and an α-helical C-terminal domain. The N-terminal domain include a positively charged region at the N-terminus that is important for the endocytosis of PrPC, octapeptide repeats that allow PrPC to bind ions, and a hydrophobic tract. The C-terminal domain consists of three α-helices and two short β-strands. This domain is also the site of posttranslational modifications in PrPC; up to two N-glycans are added to the α-helical domain, and a GPI anchor at the C-terminus attaches PrPC to the outer surface of the plasma membrane. (B) The three-dimensional structure of residues 90-31 of recombinant human PrPC (PDB #2lsb.1.A), as determined by NMR spectroscopy.