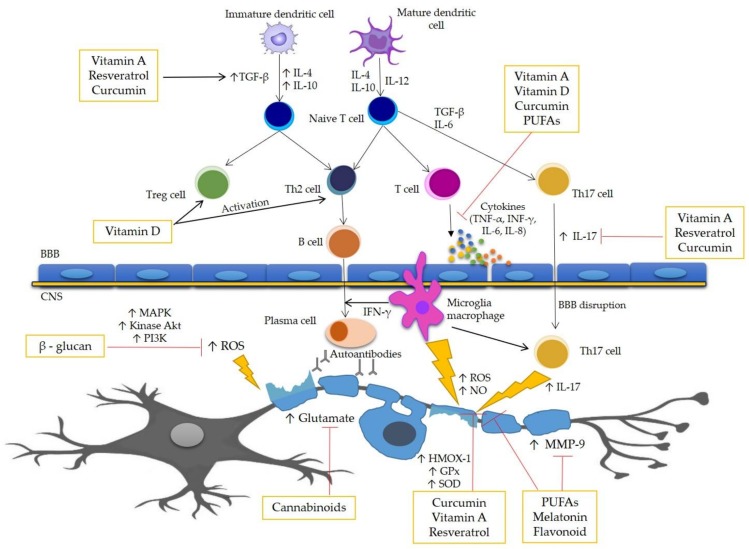
Figure 1.
Pathomechanism of MS and potential action site of bioactive compounds. One of the major factors in the pathogenesis of MS is oxidative stress, enhancing inflammation and in consequence causing damage of the myelin sheath and death of the neurons. The course of MS is associated with the secretion of many inflammatory and oxidative stress mediators, including cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, TNF-α, and INF-γ. The process of demyelination is caused by the action of many cells of the immune system mainly by macrophages, B-cells, and T cells, as well as the increased permeability of the blood–brain barrier (BBB). This figure represents the scheme of the potential action site of the bioactive antioxidant compounds.