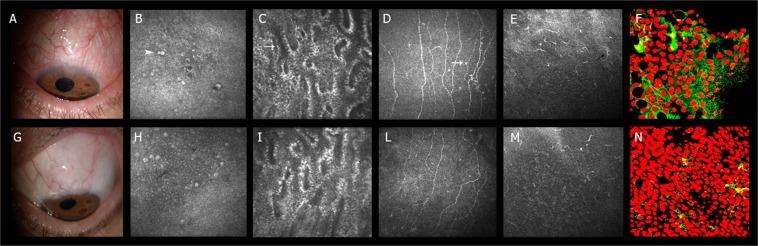
Figure 1.
Ocular surface modifications after completely successful glaucoma filtration surgery. (A–F) Baseline assessment of the ocular surface and eyelids (A) in a patient candidate to filtration surgery. (B–E) indicate the confocal microscopy appearance of conjunctival GCs (arrowhead), MG and SCN patterns of inhomogeneity (hyper-reflective points, white arrow), and limbal DCs (black arrow), respectively. F shows the IC of the conjunctiva with the HLA-DR positivity represented in green. (G–N) Post-surgical assessment of the ocular surface and eyelids (G). At six months, GCs increased their density (H), whereas the MG and SCN patterns of inhomogeneity (I,L), the limbal DC density (M) and the conjunctival HLA-DR positivity (N), reduced.