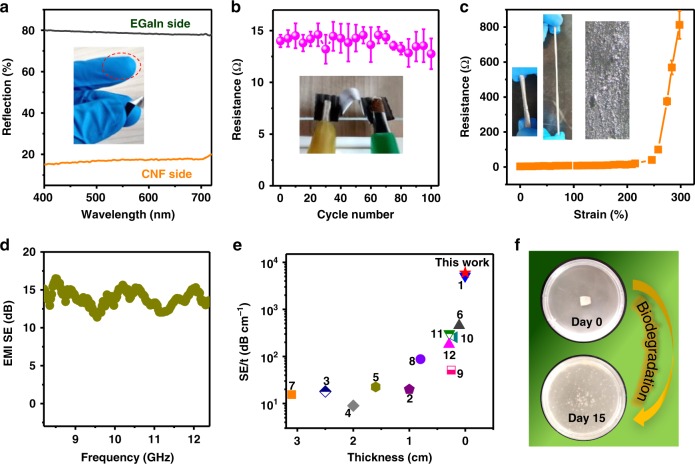
Fig. 2.
Physical characterisation of Janus EGaIn film and coating. a Optical reflection of CNFs-rich and EGaIn-rich sides. The inset gives endurance of EGaIn side to mild rub. b Cyclic bending endurance evaluated by electric resistance. EGaIn/CNFs layer thickness: 9/10 μm/μm. Bending angle 180°. c Stretching conductivity of EGaIn-rich layer on SEBS. EGaIn layer: 10 μm. The inset gives optical observation before (Left) and after (Middle & Right) stretching. d Electromagnetic shielding efficiency (EM SE) of EGaIn-rich layer after sintering. EGaIn/CNFs layer thickness: 10/10 μm/μm. e Comparison of SE/t as function of thickness t. 1: Ti3C2Tx/cellulose26; 2: Graphene/PDMS32; 3: Reduced graphene oxide (rGO)37; 4: Carbon black/rubber28; 5: Carbon nanowires/graphene/PDMS34; 6: Carbon nanotube (CNT)/acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene29; 7: Steel/PP33; 8: rGO/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)31; 9: rGO/polyetherimide30; 10: Carbon/phthalonitrile36; 11: Ni/polyethersulfone35; 12: Carbon nanofibers27. f Biological degradation of free-standing film in soil extract for 0 and 15 days