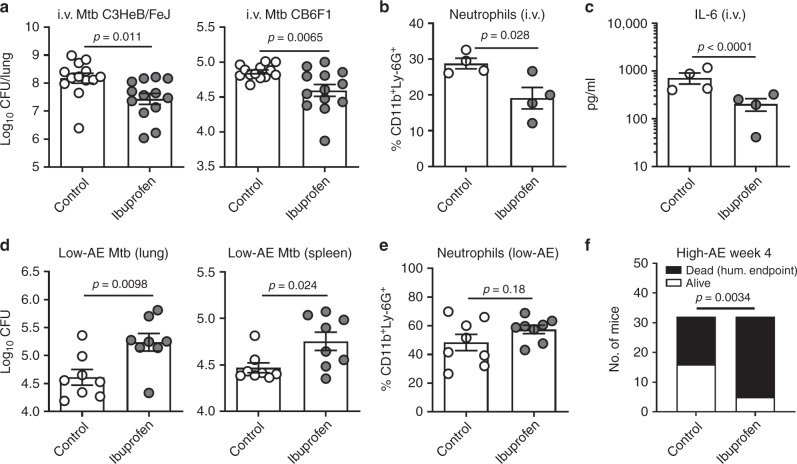
Fig. 2.
The COXi treatment effect is dependent on route of infection, not a specific COX1/2 inhibitor. a Female C3HeB/FeJ or CB6F1 mice of 6 to 8-weeks of age were infected by intravenous (i.v.) injection of 5 × 104 Mtb H37Rv or Erdman respectively. After 3 weeks, the animals were put on a 1-week course of 80 mg/day oral ibuprofen before enumerating Mtb bacilli in the lungs (n = 13). b The frequency of neutrophils in the lungs of C3HeB/FeJ mice (n = 4) was determined by flow cytometry gating on CD11b+/Ly-6G+ cells 1 week after treatment. c Soluble IL-6 was measured along with other pro-inflammatory cytokines (Supplementary Fig. 3) by multiplex analysis of lung homogenates of C3HeB/FeJ mice after 1 week of treatment (n = 4). For this analysis, q values (adjusted p values) were calculated with an ANOVA followed by the Benjamini-Hochberg method to control the false discovery rate during multiple comparisons. d 6 to 8-week-old female CB6F1 mice were infected with a low dose of ~25–50 CFU Mtb Erdman by the aerosol (AE) route and put on a course of 80 mg/day oral ibuprofen at week 4 of the infection (as in Fig. 1). After 8 weeks of treatment (week 12 of the infection), Mtb bacilli were enumerated in both lungs and spleen by plating organ homogenates (n = 8). Data is shown from one out of two independent experimentswith n = 8 and n = 6, respectively. e Two weeks into the treatment (week 6 of the infection) the frequency of neutrophils in the lungs was determined as before (data from one representative experiment, n = 8). f 6 to 8-week-old female CB6F1 mice were infected with a high-dose of ~150–300 CFU Mtb Erdman by the aerosol (AE) route and put on a course of 80 mg/day oral ibuprofen at week 3 of the infection. Mice were monitored individually for 1 week and euthanized when they reached pre-defined humane endpoints. The p value was calculated using a chi-square test. Bars represent mean ± SEM and p values were calculated with an unpaired two-tailed t-test comparing treated and non-treated animals (unless otherwise indicated)