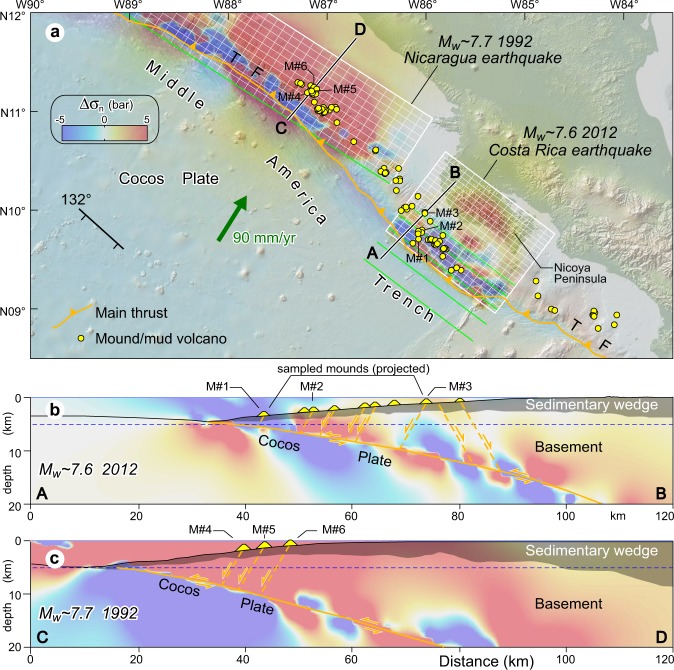
Figure 3.
(a) Normal stress changes (Δσn; bar, fault unclamping positive) created by the 2012 Costa Rica and 1992 Nicaragua earthquakes (finite fault models from Hayes34,36; symbols are as those in Fig. 2); see also Fig. S2 and Supporting Information. Small yellow circles indicate different types of seafloor methane seeps (after Ranero et al.18 and Kluesner et al.22). (b,c) Vertical cross sections of normal stress changes superposed onto the Costa Rica18 and Nicaragua33 wedges (sedimentary wedge in gray shading). The emitted fluids are inferred to travel upward along normal faults rooted in the subduction interface, and thus stress changes are resolved on seaward-dipping normal faults (strike = 132°, dip = 60°, rake = −90°). A convenient range of stress change values (−5, 5 bar) has been arbitrarily chosen; note that in some models the calculated stresses may exceed this range. In horizontal section a stress is sampled at 5 km depth (dashed blue line in vertical cross sections b and c). This figure was generated using the Coulomb 3.4 software (https://earthquake.usgs.gov/research/software/coulomb) and Adobe Illustrator CS3 (https://www.adobe.com).