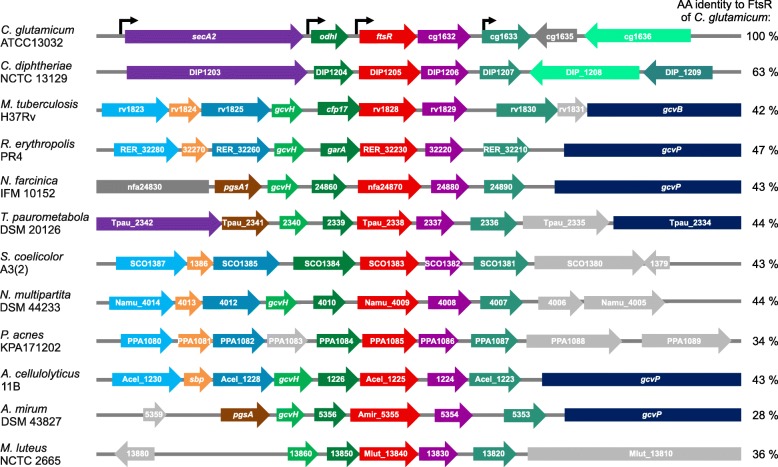
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic conservation of ftsR (cg1631) and adjacent genes. ftsR and its homologs in different actinobacterial species of various genera are shown in red. Neighboring homologous genes are colored alike, whereas grey arrows indicate genes that are not conserved in the gene cluster analyzed. The black arrows indicate transcriptional start sites determined by RNA-Seq for C. glutamicum [29]. Note that the four-gene-cluster comprising ftsR, its upstream gene odhI/garA, and the two downstream genes encoding a bifunctional nuclease and a MerR-type transcriptional regulator is strongly conserved. The figure was prepared based on data of MicrobesOnline [30] and ERGO [31]. The amino acid sequence identity of the C. glutamicum FtsR homologs is given on the right and was derived from NCBI BLAST [32]. For lack of space, some locus tag prefixes were omitted in short genes. Gene lengths are approximately to scale. The full species names are as following: Corynebacterium glutamicum, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Rhodococcus erythropolis, Nocardia farcinica, Tsukamurella paurometabola, Streptomyces coelicolor, Nakamurella multipartita, Propionibacterium acnes, Acidothermus cellulolyticus, Actinosynnema mirum, Micrococcus luteus